Textbook Question
Draw an energy diagram for an exothermic reaction.
2444
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
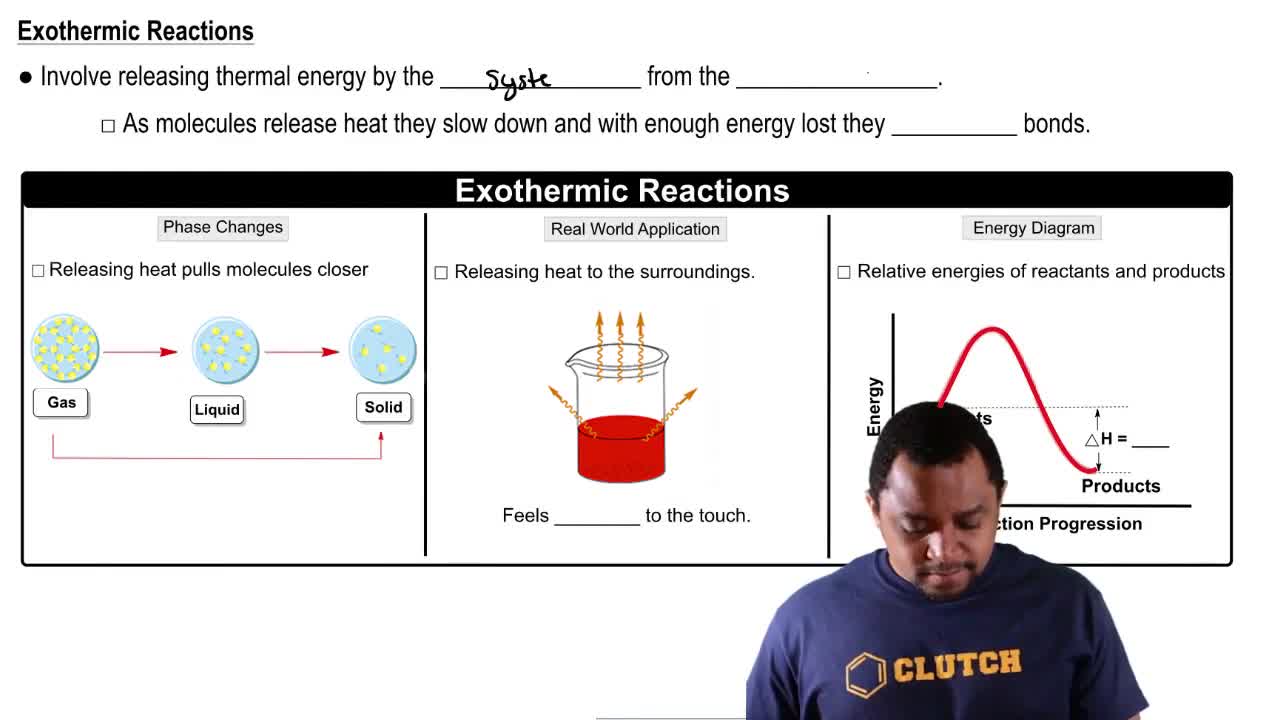
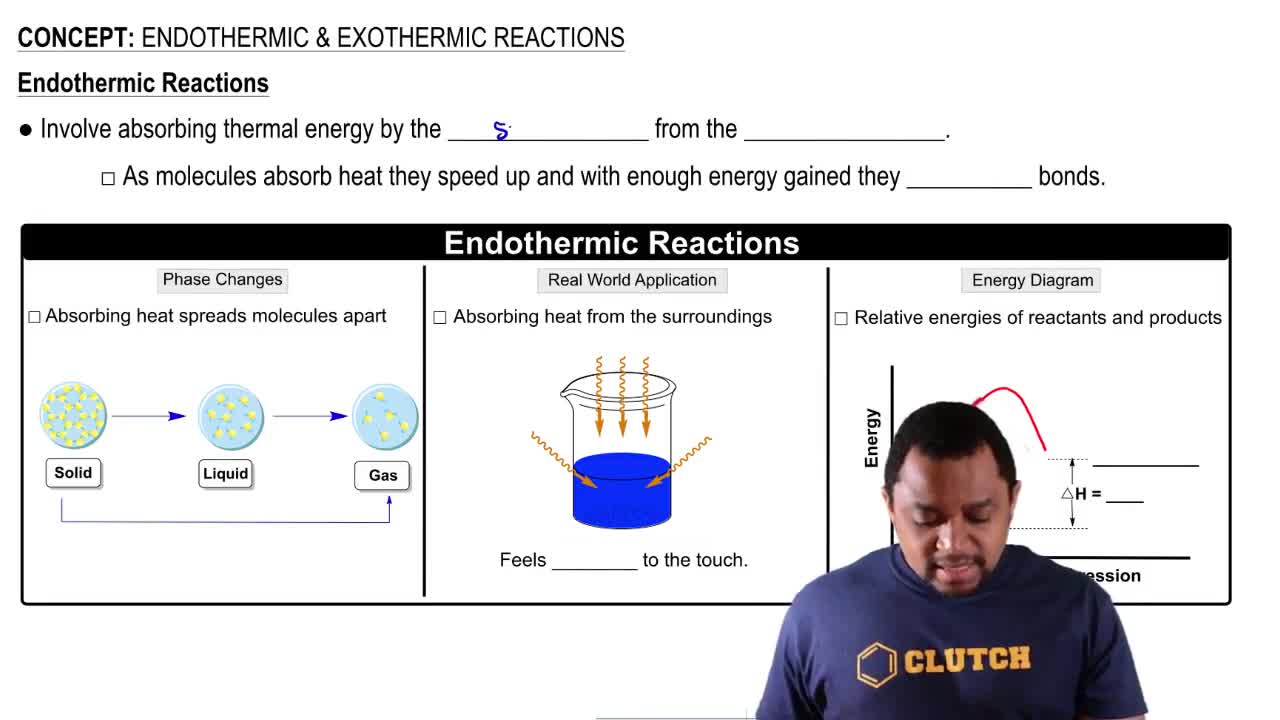

Draw an energy diagram for an exothermic reaction.
What is measured by the heat of reaction?
Classify each of the following as exothermic or endothermic:
b. The energy level of the products is higher than that of the reactants.
Classify each of the following as exothermic or endothermic:
b. In the body, the synthesis of proteins requires energy.
Classify each of the following as exothermic or endothermic:
a. CH4(g) + 2O2(g) CO2(g) + 2H2O(g) + 802kJ
What is meant by the rate of a reaction?