During a procedure on Ms. Norman's pancreas, a surgeon makes the initial incision in the left anterior hypochondriac region. List all the organs, serous membranes, and body cavities that the surgeon will encounter as she moves through the body to get to the pancreas. (Hint: Refer to A&P in the Real World: Abdominal Pain for help.)
Ch. 1 Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology

Erin C. Amerman2nd EditionHuman Anatomy & PhysiologyISBN: 9780136873822Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 1, Problem L2.2
Use the correct regional and directional terms to describe the location of each of the following organs in the body. You may use Figure 1.8 for reference. <IMAGE>
a. Esophagus
b. Brain
c. Urinary bladder (in a female)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Step 1: Understand the regional and directional terms used in anatomy. Regional terms refer to specific areas of the body (e.g., thoracic for the chest, cranial for the head), while directional terms describe the location of one structure relative to another (e.g., superior, inferior, anterior, posterior).
Step 2: For the esophagus, identify its location in the body. The esophagus is a muscular tube that connects the throat (pharynx) to the stomach. It is located in the thoracic region and is posterior to the trachea. Use the terms 'thoracic' and 'posterior' to describe its location.
Step 3: For the brain, determine its position in the cranial cavity. The brain is located in the cranial region, which is part of the dorsal body cavity. It is superior to the spinal cord and enclosed within the skull. Use the terms 'cranial' and 'superior' to describe its location.
Step 4: For the urinary bladder in a female, identify its position in the pelvic cavity. The urinary bladder is located in the pelvic region, anterior to the rectum and inferior to the uterus. Use the terms 'pelvic,' 'anterior,' and 'inferior' to describe its location.
Step 5: Cross-reference Figure 1.8 (or a similar anatomical diagram) to confirm the accuracy of the regional and directional terms used for each organ. This ensures that the descriptions align with standard anatomical terminology.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Regional Terms
Regional terms are specific anatomical terms used to describe the locations of various body parts in relation to one another. These terms help in identifying areas of the body, such as 'thoracic' for the chest region or 'abdominal' for the stomach area. Understanding these terms is essential for accurately describing the position of organs like the esophagus, brain, and urinary bladder.
Recommended video:
Guided course
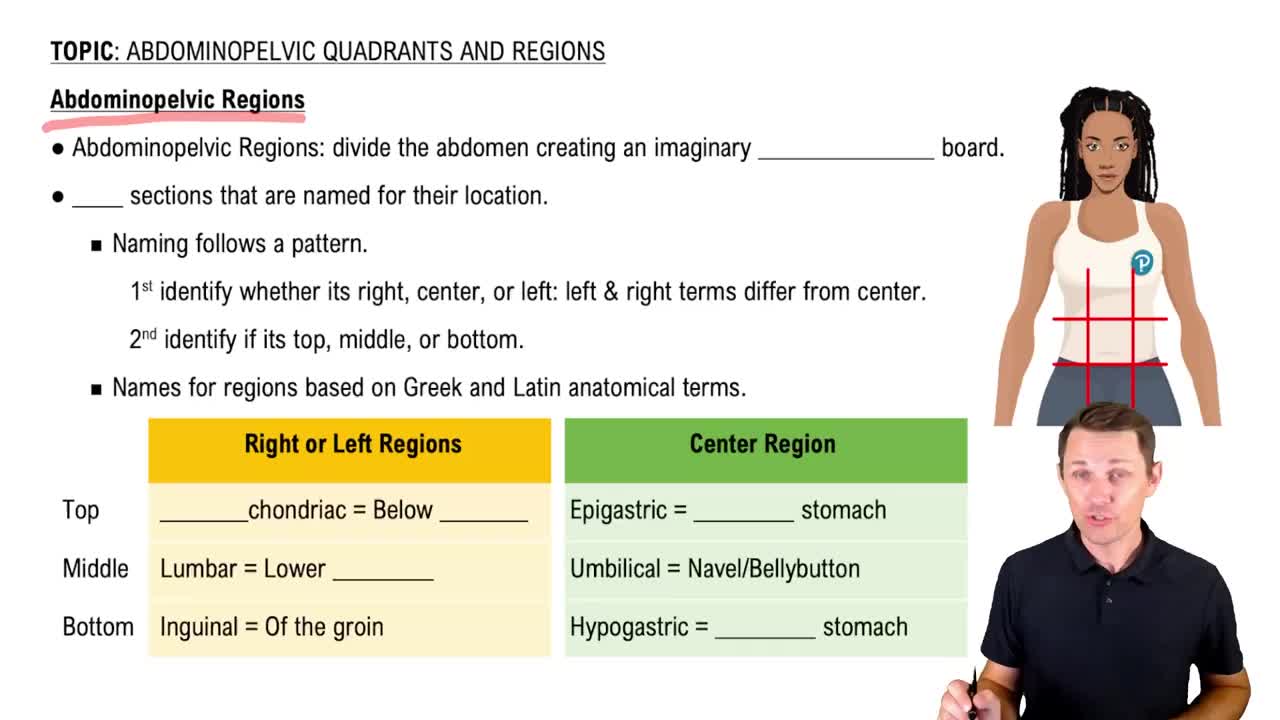
The 9 Abdominopelvic Regions
Directional Terms
Directional terms are used to explain the position of one body part relative to another. Common examples include 'superior' (above), 'inferior' (below), 'anterior' (front), and 'posterior' (back). These terms are crucial for providing clear and precise descriptions of organ locations, such as stating that the brain is superior to the spinal cord.
Recommended video:
Guided course
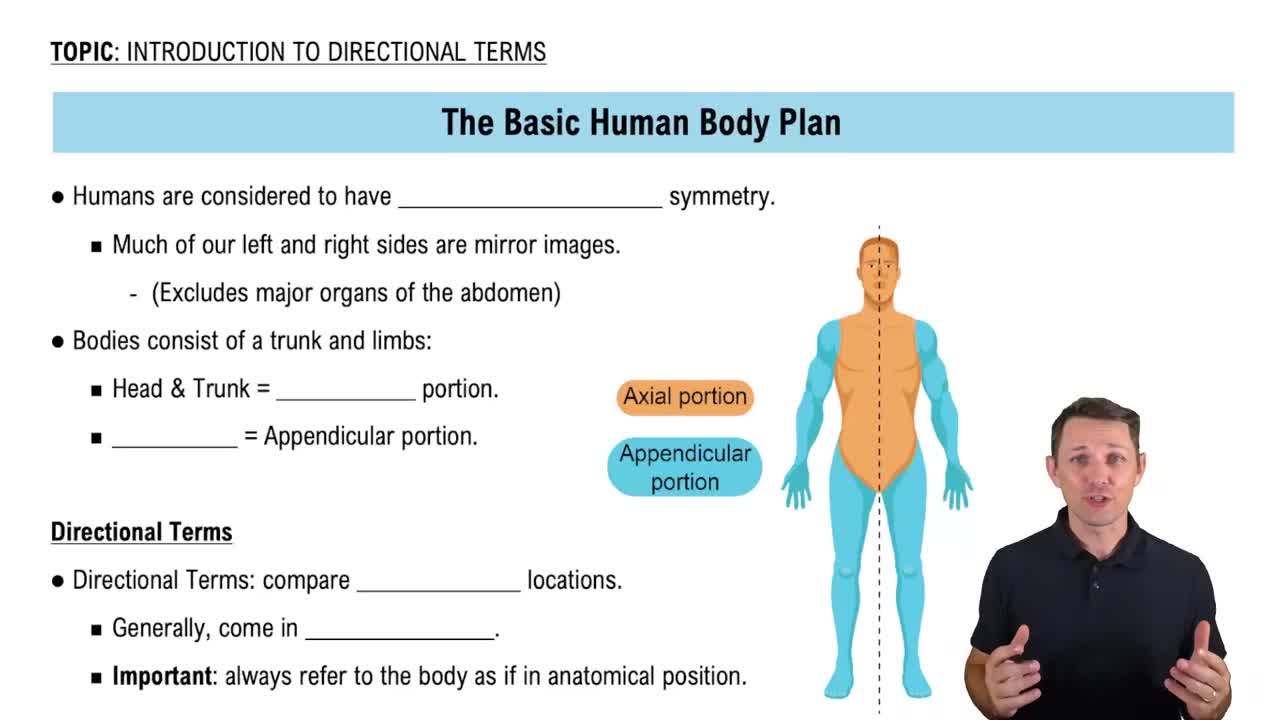
Introduction to Directional Terms
Anatomical Position
The anatomical position is a standard reference point used in anatomy to describe the locations of body parts. In this position, a person stands upright, facing forward, with arms at the sides and palms facing forward. This position serves as a baseline for using regional and directional terms, ensuring consistency in anatomical descriptions, such as the relative positions of the esophagus and urinary bladder.
Recommended video:
Guided course
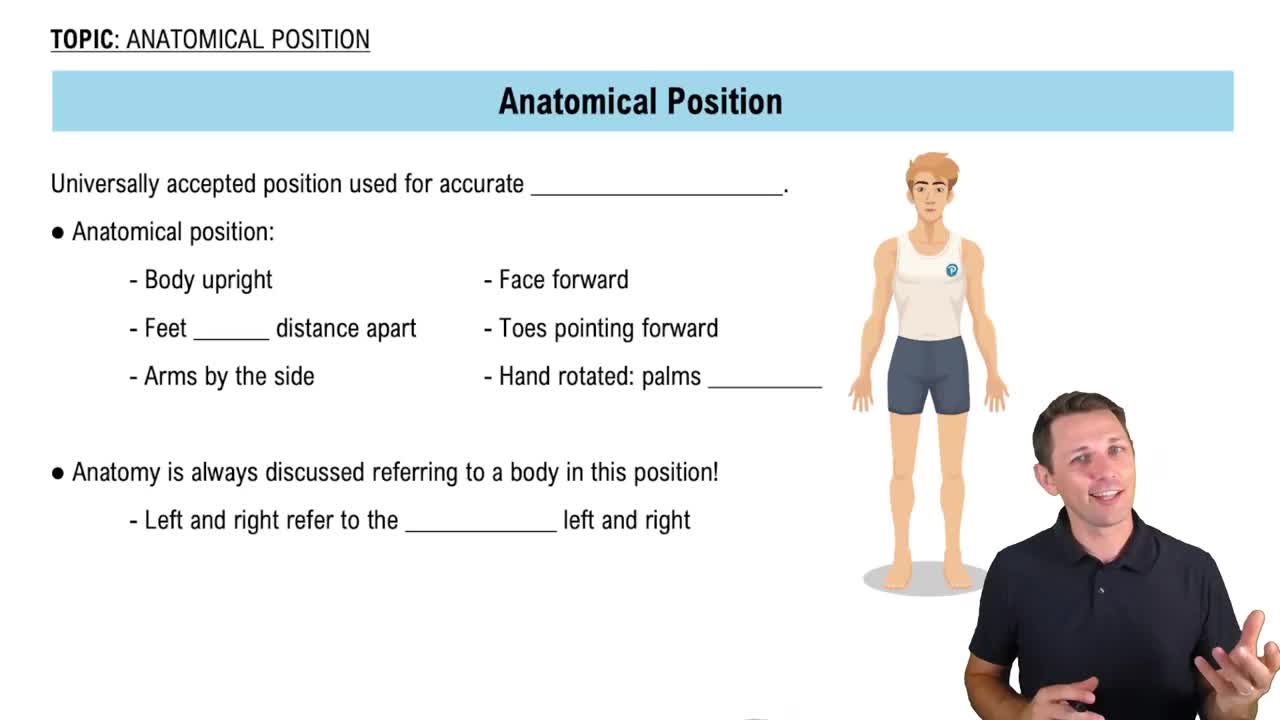
Anatomical Position
Related Practice
Textbook Question
705
views
Textbook Question
Later that same day, the surgeon performs a procedure on Ms. Norman's right kidney. She makes the incision in the right posterior lumbar region. Will she cut through the same serous membrane(s) and cavities as in the previous procedure? Why or why not? How would this change if the incision were made on the anterior lumbar region?
446
views
Textbook Question
Ms. Norman presents to the clinic with right upper quadrant pain. Predict the organs and cavities that may be involved in causing her pain.
486
views
Textbook Question
The baroreceptor reflex causes blood pressure to drop when it rises dangerously high. Predict whether this is a positive or negative feedback loop. Explain your reasoning.
869
views
Textbook Question
The study of the form of the body is_______; the study of its functions is__________.
1673
views
3
rank
