An experimental toxin makes the refractory period of cardiac muscle cells equal in length to that of skeletal muscle fibers. Predict the consequences of this toxin.

The pericardial cavity is located between:
a. The parietal pericardium and the fibrous pericardium.
b. The fibrous pericardium and the myocardium.
c. The parietal pericardium and the visceral pericardium.
d. The epicardium and the endocardium.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Pericardial Cavity
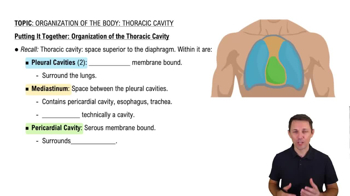
Pericardium Layers

Heart Anatomy

Mark the following statements as true or false. If a statement is false, correct it to make a true statement.
The heart consists of two superior ventricles and two inferior atria.
Mark the following statements as true or false. If a statement is false, correct it to make a true statement.
The heart plays a role in the regulation of blood pressure and secretes the hormone atrial natriuretic peptide.
Which of the following statements is true?
a. The tricuspid valve is located between the right atrium and the right ventricle.
b. The mitral valve is located between the pulmonary veins and the left atrium.
c. The pulmonary valve is located between the pulmonary artery and the pulmonary veins.
d. The aortic valve is located between the right ventricle and the aorta.
How do pacemaker cardiac muscle cells differ from contractile cardiac muscle cells? What is autorhythmicity?
Cardiac muscle cells are joined by structures called:
a. T-tubules.
b. tight junctions.
c. sarcoplasmic reticulum.
d. intercalated discs.
