Textbook Question
Organic chemistry is currently defined as
a. The study of compounds made only by living cells.
b. The study of carbon compounds.
c. The study of natural (as opposed to synthetic) compounds.
d. The study of hydrocarbons.
2285
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance



Organic chemistry is currently defined as
a. The study of compounds made only by living cells.
b. The study of carbon compounds.
c. The study of natural (as opposed to synthetic) compounds.
d. The study of hydrocarbons.
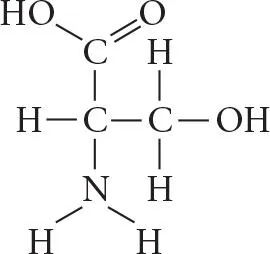
Which chemical group is most likely to be responsible for an organic molecule behaving as a base?
a. Hydroxyl
b. Carbonyl
c. Amino
d. Phosphate
Visualize the structural formula of each of the following hydrocarbons. Which hydrocarbon has a double bond in its carbon skeleton?
a. C3H8
b. C₂H₆
c. C₂H₄
d. C₂H₂
Choose the term that correctly describes the relationship between these two sugar molecules:
a. Structural isomers
b. Cis-trans isomers
c. Enantiomers
d. Isotopes