How can dinoflagellates be harmful to humans? a. They are transmitted by mosquitoes and cause malaria. b. They produce toxins that can be absorbed by clams and other shellfish which, when eaten by people, can lead to paralytic shellfish poisoning. c. They cause amoebic dysentery which leads to severe diarrhea and dehydration. d. They are transmitted by tsetse flies and cause 'sleeping sickness.'

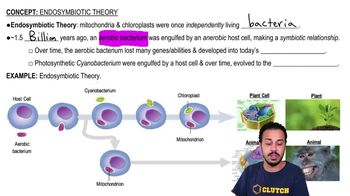
Why was finding a close relationship between mitochondrial DNA and bacterial DNA considered particularly strong evidence in favor of the endosymbiosis theory?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
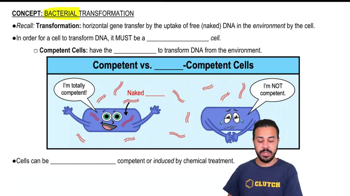
Key Concepts
Mitochondrial DNA

Bacterial DNA
Endosymbiosis Theory
Explain the logic behind the claim that the nuclear envelope is a synapomorphy that defines eukaryotes as a monophyletic group.
Consider the endosymbiosis theory for the origin of the mitochondrion. How did each endosymbiotic partner benefit from the relationship?
The text claims that the evolutionary history of protists can be understood as a series of morphological innovations that established seven distinct lineages, each of which subsequently diversified based on innovative ways of feeding, moving, and reproducing. Explain how the Alveolata support this claim.
Consider the following:
Plasmodium has an unusual organelle called an apicoplast. Recent research has shown that apicoplasts are derived from chloroplasts via secondary endosymbiosis and have a large number of genes related to chloroplast DNA.
Glyphosate is one of the most widely used herbicides. It works by poisoning an enzyme located in chloroplasts.
Biologists are testing the hypothesis that glyphosate could be used as an antimalarial drug in humans.
How are these observations connected?
Suppose a friend says that we don't need to worry about the rising temperatures associated with global climate change. She claims that increased temperatures will make planktonic algae grow faster and that carbon dioxide (CO2) will be removed from the atmosphere faster. According to her, this carbon will be buried at the bottom of the ocean in calcium carbonate shells. As a result, the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere will decrease and global warming will decline. Comment.
