Textbook Question
The U.S. quarter has a mass of 5.67 g and is approximately 1.55 mm thick. (a) How many quarters would have to be stacked to reach 575 ft, the height of the Washington Monument?
1587
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

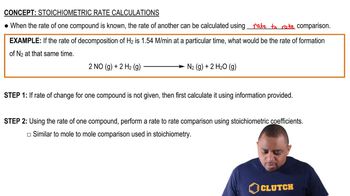
The U.S. quarter has a mass of 5.67 g and is approximately 1.55 mm thick. (a) How many quarters would have to be stacked to reach 575 ft, the height of the Washington Monument?
The U.S. quarter has a mass of 5.67 g and is approximately 1.55 mm thick. (c) How much money would this stack contain?
The U.S. quarter has a mass of 5.67 g and is approximately 1.55 mm thick.(d) The U.S. National Debt Clock showed the outstanding public debt to be \$16,213,166,914,811 on October 28, 2012. How many stacks like the one described would be necessary to pay off this debt?