Why did geneticists believe, even before direct experimental evidence was obtained, that the genetic code would turn out to be composed of triplet sequences and be nonoverlapping? Experimentally, how were these suppositions shown to be correct?
Ch. 13 - The Genetic Code and Transcription

Chapter 13, Problem 1d
How were the experimentally derived triplet codon assignments verified in studies using bacteriophage MS2?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand that the bacteriophage MS2 system was used to experimentally verify the genetic code by synthesizing RNA sequences with known nucleotide compositions and observing the resulting polypeptides.
Recognize that researchers created synthetic RNA molecules with repeating triplet sequences (e.g., repeating codons like UUU, AAA, or CCC) and introduced these RNAs into a cell-free translation system derived from bacteriophage MS2-infected cells.
Observe the polypeptides produced from these synthetic RNAs, identifying the amino acids incorporated by analyzing the protein products, often using techniques like chromatography or electrophoresis.
Correlate the known synthetic RNA triplet sequences with the amino acid sequences of the resulting polypeptides to confirm which triplet codons specify which amino acids.
Use this experimental approach to systematically verify the assignments of triplet codons to amino acids, thereby confirming the genetic code as deciphered from earlier experiments.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
1mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Triplet Codon Hypothesis
The triplet codon hypothesis states that genetic information is encoded in sequences of three nucleotides, called codons, each specifying a single amino acid. This concept is fundamental to understanding how nucleotide sequences translate into proteins.
Recommended video:
Guided course
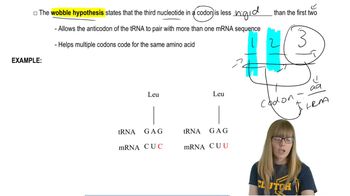
Translation:Wobble Hypothesis
Bacteriophage MS2 as a Model System
Bacteriophage MS2 is an RNA virus used as a model to study genetic coding because its genome is well-characterized and simple. Experiments with MS2 allowed researchers to link specific RNA sequences to amino acid sequences, facilitating verification of codon assignments.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Mapping Bacteriophages
Experimental Verification via Mutagenesis and Protein Analysis
Verification involved inducing mutations in the MS2 RNA and analyzing resulting changes in the viral proteins. By correlating specific nucleotide changes with altered amino acids, researchers confirmed the triplet nature of codons and their assignments.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Proteins
Related Practice
Textbook Question
500
views
Textbook Question
What experimental evidence provided the initial insights into the compositions of codons encoding specific amino acids?
632
views
Textbook Question
How were the specific sequences of triplet codes determined experimentally?
559
views
1
rank
Textbook Question
Write a short essay that summarizes the key properties of the genetic code and the process by which RNA is transcribed on a DNA template.
509
views
Textbook Question
Assuming the genetic code is a triplet, what effect would the addition or loss of two nucleotides have on the reading frame? The addition or loss of three, six, or nine nucleotides?
951
views
Textbook Question
The mRNA formed from the repeating tetranucleotide UUAC incorporates only three amino acids, but the use of UAUC incorporates four amino acids. Why?
704
views
