Show the dipole arrow for each of the following bonds:
a. Si―Cl

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

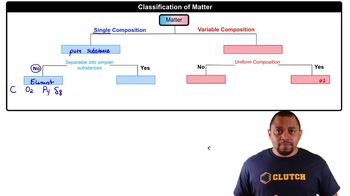
Show the dipole arrow for each of the following bonds:
a. Si―Cl
Calculate the electronegativity difference and classify each of the following bonds as nonpolar covalent, polar covalent, or ionic:
a. Si and Cl
Calculate the electronegativity difference and classify each of the following bonds as nonpolar covalent, polar covalent, or ionic:
b. C and C
Predict the shape and polarity of each of the following molecules, which have polar covalent bonds:
a. A central atom with three identical bonded atoms and one lone pair.
Identify the group number in the periodic table of X, a representative element, in each of the following ionic compounds:
a. XCl3
Identify the group number in the periodic table of X, a representative element, in each of the following ionic compounds:
b. Al2X3