Textbook Question
What are some conditions that characterize ketosis?
1045
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

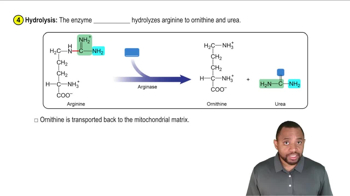

What are some conditions that characterize ketosis?
Draw the condensed structural formula for the α-keto acid produced from each of the following in transamination:
a.
Why does the body convert NH4+ to urea?
What metabolic substrate(s) are produced from the carbon atoms of each of the following amino acids?
c. tyrosine
What metabolic substrate(s) are produced from the carbon atoms of each of the following amino acids?
b. asparagine
Draw the condensed structural formulas for the products of the reaction of aspartate and α-ketoglutarate which is catalyzed by aspartate transaminase (AST).