Textbook Question
Calculate the pH of each solution given the following:
c. [OH-] = 1 × 10-5 M
883
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance



Calculate the pH of each solution given the following:
c. [OH-] = 1 × 10-5 M
Calculate the pH of each solution given the following:
f. [OH-] = 8.2 × 10-4 M
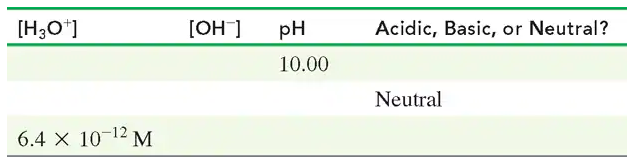
Complete the following table:
Complete and balance the equation for each of the following reactions:
a. ZnCO3(s) + HBr(aq) →
Complete and balance the equation for each of the following reactions:
b. Zn(s) + HCl(aq) →
Complete and balance the equation for each of the following reactions:
c. HCl(aq) + NaHCO3(s) →