Describe the formation of an aqueous KI solution, when solid KI dissolves in water.

Write a balanced equation for the dissociation of each of the following strong electrolytes in water:
d. Fe(NO3)3
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
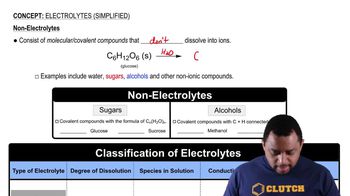
Dissociation of Electrolytes
Ionic Compounds

Balanced Chemical Equations

Water is a polar solvent and carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) is a nonpolar solvent. In which solvent is each of the following, which is found or used in the body, more likely to be soluble?
d. cholesterol (lipid), nonpolar
KF is a strong electrolyte, and HF is a weak electrolyte. How is the solution of KF different from that of HF?
Indicate whether aqueous solutions of each of the following solutes contain only ions, only molecules, or mostly molecules and a few ions:
a. acetic acid, HC2H3O2, a weak electrolyte
Indicate whether aqueous solutions of each of the following solutes contain only ions, only molecules, or mostly molecules and a few ions:
b. NaBr, a strong electrolyte
Indicate whether aqueous solutions of each of the following solutes contain only ions, only molecules, or mostly molecules and a few ions: c. fructose, C6H12O6, a nonelectrolyte
