A portion of a polypeptide chain contains the following sequence of amino acids:
—Leu—Val—Cys—Asp—
c. How does the primary structure of a protein affect its tertiary structure?

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
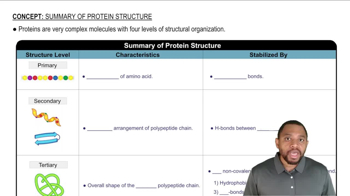

A portion of a polypeptide chain contains the following sequence of amino acids:
—Leu—Val—Cys—Asp—
c. How does the primary structure of a protein affect its tertiary structure?
In myoglobin, about one-half of the 153 amino acids have nonpolar R groups.
a. Where would you expect those amino acids to be located in the tertiary structure?
In myoglobin, about one-half of the 153 amino acids have nonpolar R groups.
b. Where would you expect the polar R groups to be in the tertiary structure?
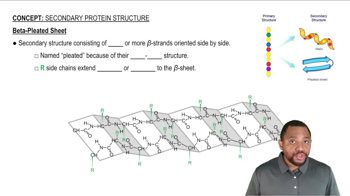
Indicate whether each of the following statements describes primary, secondary, tertiary, or quaternary protein structure:
b. Protein chains of collagen form a triple helix.
Indicate the changes in secondary and tertiary structural levels of proteins for each of the following:
b. Prior to giving an injection, the skin is wiped with an alcohol swab.
Indicate the changes in secondary and tertiary structural levels of proteins for each of the following:
c. To avoid spoilage, seeds are treated with a solution of HgCl2.