Textbook Question
Identify each of the following as an acid or a base:
d. HI
1156
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
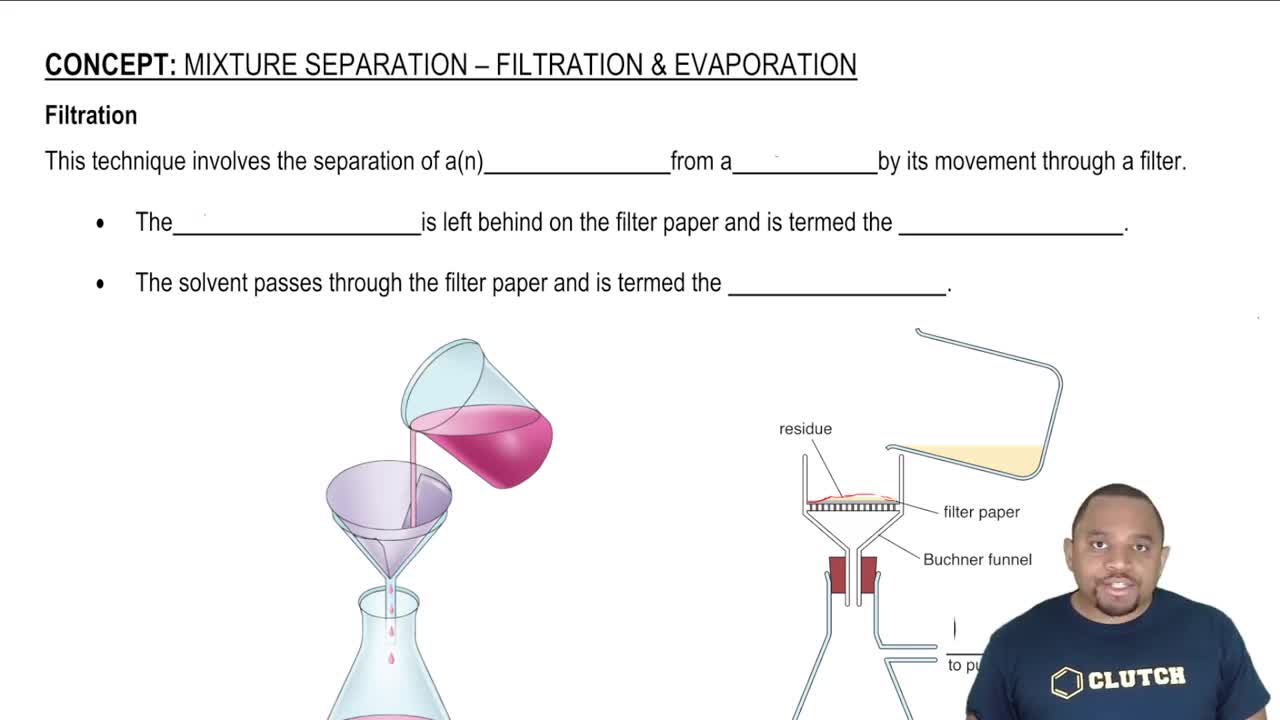
Identify each of the following as an acid or a base:
d. HI
Identify each of the following as an acid or a base:
b. H2SO3
Determine if each of the following diagrams represents a strong acid or a weak acid. The acid has the formula HX.
Sometimes, during stress or trauma, a person can start to hyperventilate. Then the person might breathe into a paper bag to avoid fainting.
b. How does breathing into a paper bag help return blood pH to normal?
<IMAGE>
Identify each of the following as an acid, base, or salt, and give its name:
e. H2CO3
Identify each of the following as an acid, base, or salt, and give its name:
a. H3PO4