Textbook Question
Match each of the following physical and chemical properties with ethane, C2H6 or sodium bromide, NaBr:
b. burns vigorously in air
34
views

 Timberlake 13th Edition
Timberlake 13th Edition Ch.11 Introduction to Organic Chemistry: Hydrocarbons
Ch.11 Introduction to Organic Chemistry: Hydrocarbons Problem 10c
Problem 10c Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


Match each of the following physical and chemical properties with ethane, C2H6 or sodium bromide, NaBr:
b. burns vigorously in air
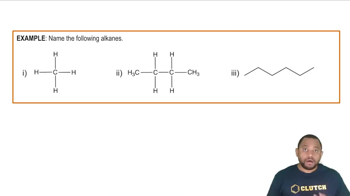
Give the IUPAC name for each of the following alkanes and cycloalkanes:
a. <IMAGE>
Give the IUPAC name for each of the following alkanes and cycloalkanes:
c.
Indicate whether each of the following pairs represent structural isomers or the same molecule:
a.
Indicate whether each of the following pairs represent structural isomers or the same molecule:
b.
Give the IUPAC name for each of the following:
b.