Textbook Question
Avobenzone is a common ingredient in sunscreen. Its structural formula is shown.
a. What functional groups are in avobenzone?
1208
views

 Timberlake 13th Edition
Timberlake 13th Edition Ch.12 Alcohols, Thiols, Ethers, Aldehydes, and Ketones
Ch.12 Alcohols, Thiols, Ethers, Aldehydes, and Ketones Problem 40
Problem 40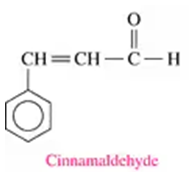
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance



Avobenzone is a common ingredient in sunscreen. Its structural formula is shown.
a. What functional groups are in avobenzone?
Avobenzone is a common ingredient in sunscreen. Its structural formula is shown.
b. What is the molecular formula and molar mass of avobenzone?
A compound called resveratrol is an antioxidant, found in the skin of grapes. Identify the functional groups in resveratrol.
<IMAGE>
Which of the following will give a positive Tollens' test?
a. propanal
b. ethanol
c. ethyl methyl ether
Which of the following will give a positive Tollens' test?
a. 1-propanol
b. 2-propanol
c. hexanal
Give the IUPAC name for each of the following alcohols and phenols:
a.