Textbook Question
Draw the Fischer projection for the oxidation and the reduction products of D-arabinose. What are the names of the sugar acid and the sugar alcohol produced?
704
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


Draw the Fischer projection for the oxidation and the reduction products of D-arabinose. What are the names of the sugar acid and the sugar alcohol produced?
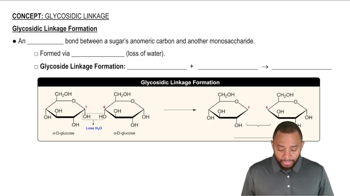
For each of the following, give the monosaccharide units produced by hydrolysis, the type of glycosidic bond, and the name of the disaccharide, including α or β:
a.
Indicate whether each disaccharide in Problem 13.41 is a reducing sugar or not.
a.
b.
Describe the similarities and differences in the following:
a. amylose and amylopectin
Describe the similarities and differences in the following:
a. amylose and cellulose
Give the name of one or more polysaccharides that matches each of the following descriptions:
a. not digestible by humans