Textbook Question
Write the IUPAC and common names, if any, of the carboxylate salts produced in problem 14.12
a. acetic acid
b. 2-methylbutanoic acid
c. 4-chlorobenzoic acid

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance



Write the IUPAC and common names, if any, of the carboxylate salts produced in problem 14.12
a. acetic acid
b. 2-methylbutanoic acid
c. 4-chlorobenzoic acid
Draw the condensed structural formula for the ester formed when each of the following reacts with methyl alcohol:
b. pentanoic acid
Draw the condensed structural formula for the ester formed when each of the following reacts with ethyl alcohol:
b. propionic acid
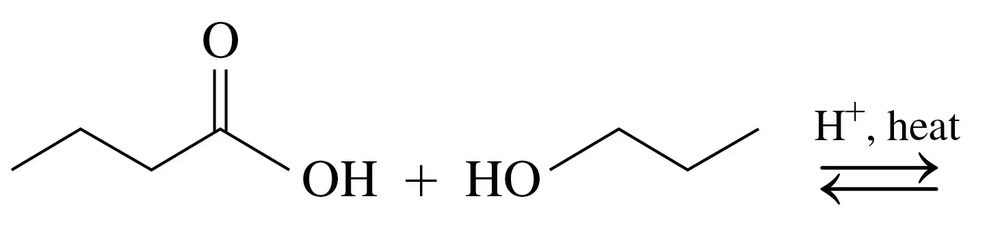
Draw the condensed structural or line-angle formula for the ester formed in each of the following reactions:
b.
Write the IUPAC and common names, if any, for each of the following:
a.
Draw the condensed structural formulas for a and b and line-angle formulas for c and d:
b. butyl formate