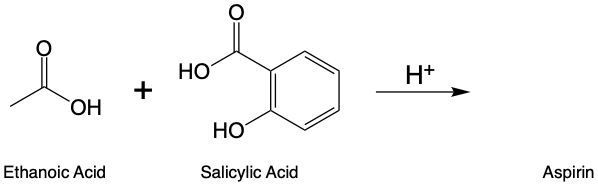
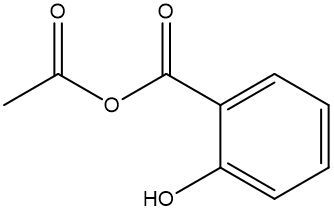
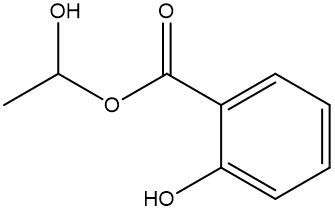
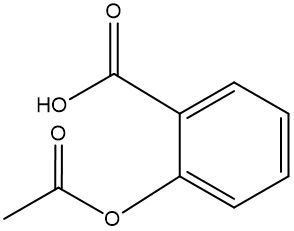
Esterification is a chemical reaction where a carboxylic acid reacts with an alcohol to form an ester through a condensation process. In this reaction, two molecules combine with the elimination of water. Specifically, the hydroxyl group (–OH) from the carboxylic acid and a hydrogen atom (H) from the alcohol are removed, resulting in the formation of water (H2O).
To initiate this reaction, an H+ catalyst is necessary. This catalyst facilitates the interaction between the carboxylic acid and the alcohol. When these two reactants come into proximity, the loss of water occurs, allowing the carbon atom from the carboxylic acid to form a new bond with the oxygen atom from the alcohol. This process results in the creation of an ester linkage.
An ester is characterized by the presence of a carbonyl group (C=O) adjacent to an oxygen atom (–O) that is further connected to another carbon atom. Thus, through the esterification process, a carboxylic acid and an alcohol are transformed into an ester, showcasing the significance of condensation reactions in organic chemistry.