Textbook Question
Use condensed structural formulas to write the balanced chemical equation for the NaOH saponification of glyceryl trimyristate (trimyristin).
641
views

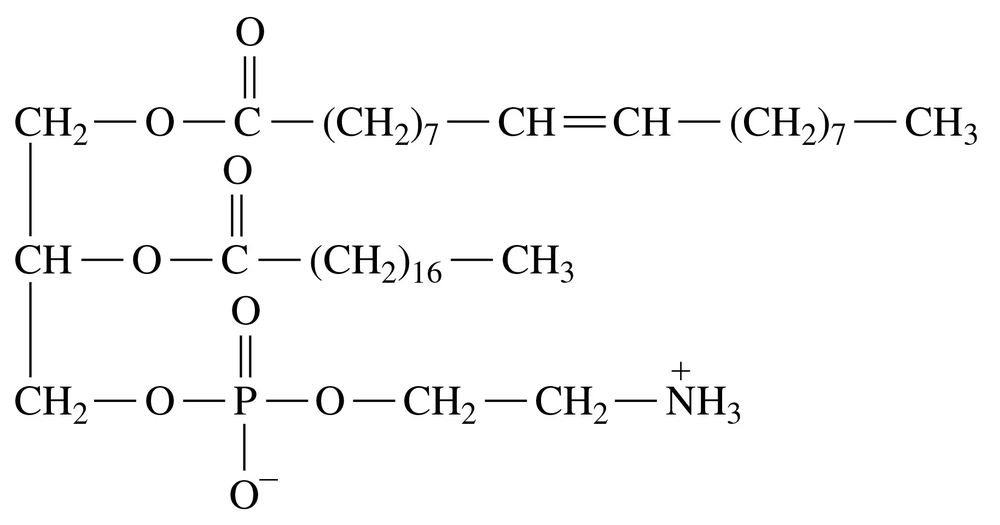
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance



Use condensed structural formulas to write the balanced chemical equation for the NaOH saponification of glyceryl trimyristate (trimyristin).
Describe the similarities and differences between triacylglycerols and glycerophospholipids.
Draw the condensed structural formula for the cephalin that contains glycerol, two palmitic acids, phosphate, and ethanolamine (ionized).
Identify the following features of this phospholipid, which is abundant in the myelin sheath that surrounds nerve cells:
b. What is the fatty acid?
Identify the following features of this phospholipid, which is needed for the brain and nerve tissues:
a. Is the phospholipid formed from glycerol or sphingosine?
Draw the structure for cholesterol.