Textbook Question
Describe the similarities and differences between triacylglycerols and glycerophospholipids.
959
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


Describe the similarities and differences between triacylglycerols and glycerophospholipids.
Draw the condensed structural formula for the cephalin that contains glycerol, two palmitic acids, phosphate, and ethanolamine (ionized).
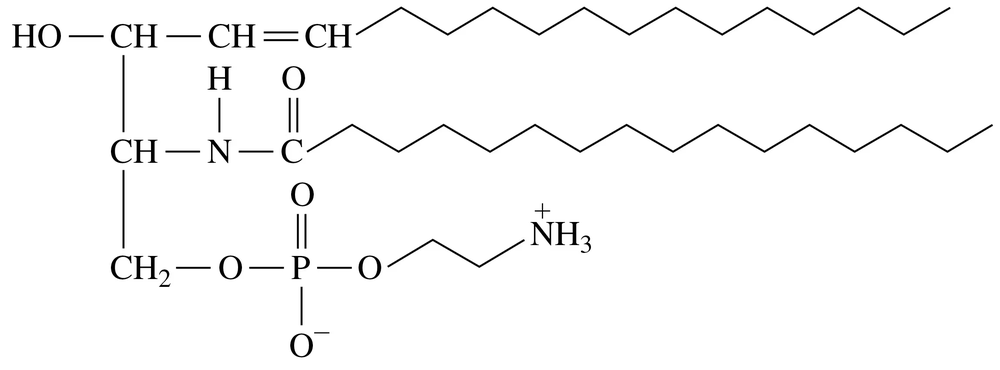
Identify the following glycerophospholipid, which is found in the nerves and spinal cord in the body, as a lecithin or cephalin, and list its components:
Identify the following features of this phospholipid, which is needed for the brain and nerve tissues:
a. Is the phospholipid formed from glycerol or sphingosine?
Draw the structure for cholesterol.
How do chylomicrons differ from VLDL?