What happens when a primary structure forms a secondary structure?
Ch.16 Amino Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes

Timberlake13th EditionChemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryISBN: 9780134421353Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 16, Problem 22a
What type of interaction would you expect between the R groups of the following amino acids in a quaternary structure?
a. phenylalanine and isoleucine
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the nature of the R groups for both amino acids. Phenylalanine has a nonpolar, aromatic R group (a benzyl group), while isoleucine has a nonpolar, aliphatic R group (a branched hydrocarbon chain).
Recall that nonpolar R groups tend to interact through hydrophobic interactions. These interactions occur because nonpolar groups avoid water and aggregate together in the interior of a protein structure.
Understand that in a quaternary structure, the hydrophobic interactions between nonpolar R groups help stabilize the overall protein structure by minimizing their exposure to the aqueous environment.
Conclude that the interaction between the R groups of phenylalanine and isoleucine in a quaternary structure would primarily be hydrophobic interactions.
Note that these hydrophobic interactions are critical for maintaining the three-dimensional structure of proteins, especially in environments where water is present.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
1mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Quaternary Structure of Proteins
The quaternary structure of proteins refers to the assembly of multiple polypeptide chains into a single functional unit. This structure is stabilized by various interactions between the R groups of the amino acids in the different chains. Understanding this concept is crucial for predicting how specific amino acids will interact in a protein complex.
Recommended video:
Guided course
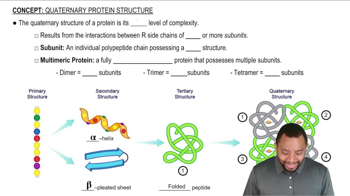
Quaternary Protein Structure Concept 1
Hydrophobic Interactions
Hydrophobic interactions occur when nonpolar R groups of amino acids, such as phenylalanine and isoleucine, come together to avoid contact with water. These interactions are a key driving force in the folding and stability of proteins, particularly in quaternary structures where multiple subunits aggregate. Recognizing these interactions helps in understanding the overall stability of protein complexes.
Recommended video:
Guided course
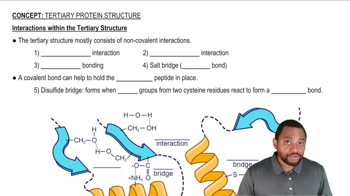
Interactions within the Tertiary Structure Concept 2
Amino Acid Properties
The properties of amino acids, determined by their R groups, influence how they interact with one another. For instance, phenylalanine has a large, nonpolar aromatic side chain, while isoleucine has a branched aliphatic side chain. These properties dictate the nature of interactions—whether they are hydrophobic, polar, or ionic—affecting the protein's structure and function.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Amino Acid Catabolism: Amino Group Example 2
Related Practice
Textbook Question
1675
views
Textbook Question
What is the difference in hydrogen bonding between an α helix and a β−pleated sheet?
1548
views
Textbook Question
What type of interaction would you expect between the R groups of the following amino acids in a tertiary structure?
c. serine and aspartate
702
views
Textbook Question
What type of interaction would you expect between the R groups of the following amino acids in a quaternary structure?
d. alanine and proline
650
views
Textbook Question
A portion of a polypeptide chain contains the following sequence of amino acids:
—Leu—Val—Cys—Asp—
a. Which amino acids are likely to be found on the inside of the protein structure? Why?
614
views
Textbook Question
A portion of a polypeptide chain contains the following sequence of amino acids:
—Leu—Val—Cys—Asp—
c. How does the primary structure of a protein affect its tertiary structure?
631
views
