Textbook Question
What are the possible codons for each of the following amino acids?
b. arginine
809
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
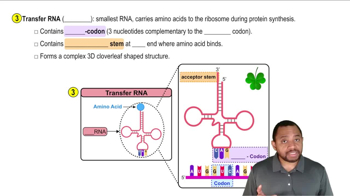
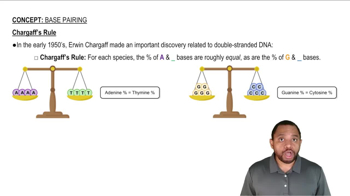
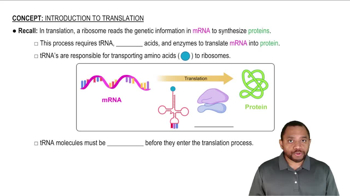
What are the possible codons for each of the following amino acids?
b. arginine
What is the amino acid for each of the following codons?
a. CAA
What is the anticodon on tRNA for each of the following codons in an mRNA?
a. AGC
Endorphins are polypeptides that reduce pain. What is the amino acid order for the endorphin leucine enkephalin (leu-enkephalin), which has the following mRNA?
AUG UAC GGU GGA UUU CUA UAA
Endorphins are polypeptides that reduce pain. What is the amino acid order for the endorphin methionine enkephalin (met-enkephalin), which has the following mRNA?
AUG UAC GGU GGA UUU AUG UAA
A polypeptide contains 36 amino acids. How many nucleotides would be found in the mRNA for this polypeptide?