Textbook Question
What is similar about the primary structure of RNA and DNA?
725
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
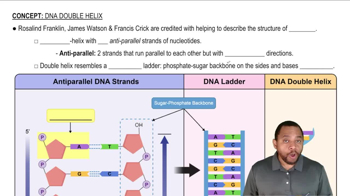

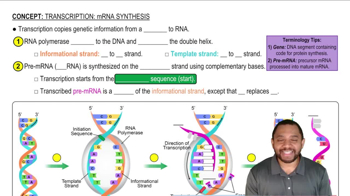
What is similar about the primary structure of RNA and DNA?
If the DNA double helix in salmon contains 28% adenine, what is the percentage of thymine, guanine, and cytosine?
In DNA, how many hydrogen bonds form between guanine and cytosine?
Match the following statements with rRNA, mRNA, or tRNA:
c. carries genetic information from the nucleus to the ribosomes
Match the following statements with rRNA, mRNA, or tRNA:
a. combines with proteins to form ribosomes
Match the following statements with rRNA, mRNA, or tRNA:
b. brings amino acids to the ribosomes for protein synthesis