What type of change, physical or chemical, takes place in each of the following?
c. A tree is cut into boards at a saw mill.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


What type of change, physical or chemical, takes place in each of the following?
c. A tree is cut into boards at a saw mill.
Water is heated to 145 °F. What is the temperature of the hot water in degrees Celsius?
During extreme hypothermia, a child's temperature dropped to 20.6 °C. What was his temperature in degrees Fahrenheit?
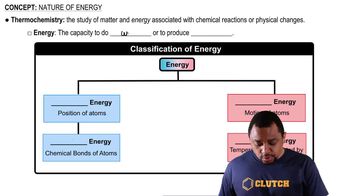
Indicate whether each of the following statements describes potential or kinetic energy:
b. kicking a ball
Indicate whether each of the following statements describes potential or kinetic energy:
c. the energy in a lump of coal
Using the energy values for foods (see TABLE 3.7), determine each of the following (round off the answer for each food type to the tens place):
d. the grams of fat in one avocado that has 405 kcal, 13 g of carbohydrate, and 5 g of protein