Textbook Question
Consider an ion with the symbol Y3- formed from a representative element.
c. If Y is in Period 3, what is the element?
965
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

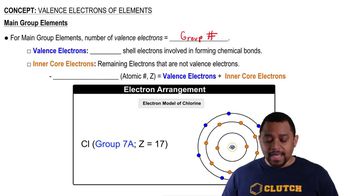
Consider an ion with the symbol Y3- formed from a representative element.
c. If Y is in Period 3, what is the element?
One of the ions of tin is tin(IV).
a. What is the symbol for this ion?
One of the ions of tin is tin(IV).
b. How many protons and electrons are in the ion?
Draw the Lewis structure for each of the following:
a. H3COCH3 (the atoms are in the order C O C)
Select the more polar bond in each of the following pairs:
c. Br―Cl or S―Cl
Show the dipole arrow for each of the following bonds:
a. Si―Cl