Write the formula including the charge for each of the following polyatomic ions:
b. sulfite

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

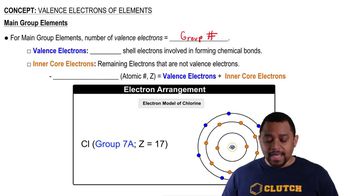
Write the formula including the charge for each of the following polyatomic ions:
b. sulfite
Name the following polyatomic ions:
c. HSO3-
Write the formula for the polyatomic ion and name each of the following compounds:
d. Fe(HCO3)3
Which electronegativity difference (a, b, or c) would you expect for a nonpolar covalent bond?
a. from 0.0 to 0.4
b. from 0.5 to 1.8
c. from 1.9 to 3.3
For each of the following bonds, indicate the positive end with 𝛿⁺ and the negative end with 𝛿⁻ . Draw an arrow to show the dipole for each.
a. N and F
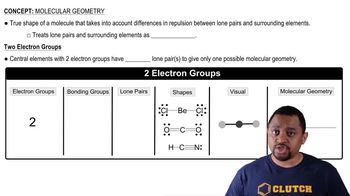
Choose the shape (1 to 6) that matches each of the following descriptions (a to c):
1. linear
2. bent (109°)
3. trigonal planar
4. bent (120°)
5. trigonal pyramidal
6. tetrahedral
b. a molecule with a central atom that has four electron groups and three bonded atoms