Write the formula for the polyatomic ion and name each of the following compounds:
d. Fe(HCO3)3

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

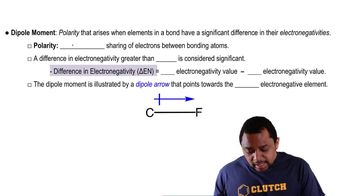
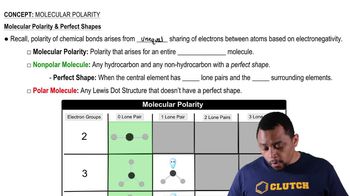
Write the formula for the polyatomic ion and name each of the following compounds:
d. Fe(HCO3)3
Draw the Lewis structure for each of the following molecules:
d. ClNO2 (N is the central atom)
Which electronegativity difference (a, b, or c) would you expect for a nonpolar covalent bond?
a. from 0.0 to 0.4
b. from 0.5 to 1.8
c. from 1.9 to 3.3
Choose the shape (1 to 6) that matches each of the following descriptions (a to c):
1. linear
2. bent (109°)
3. trigonal planar
4. bent (120°)
5. trigonal pyramidal
6. tetrahedral
b. a molecule with a central atom that has four electron groups and three bonded atoms
Complete each of the following statements for a molecule of H2S:
c. The number of atoms attached to the central S atom is _______.
Compare the Lewis structures of CF4 and NF3 Why do these molecules have different shapes?