Textbook Question
Complete each of the following statements for a molecule of H2S:
c. The number of atoms attached to the central S atom is _______.
1420
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
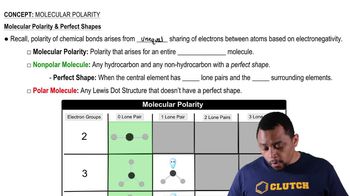

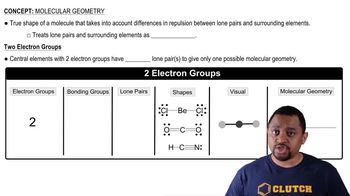
Complete each of the following statements for a molecule of H2S:
c. The number of atoms attached to the central S atom is _______.
Compare the Lewis structures of CF4 and NF3 Why do these molecules have different shapes?
Compare the Lewis structures of CH4 and H2O Why do these molecules have similar bond angles but different molecular shapes?
Identify the major type of intermolecular forces between the particles of each of the following:
b. MgF2
How does the octet rule explain the formation of a magnesium ion?
What noble gas has the same electron arrangement as the magnesium ion?