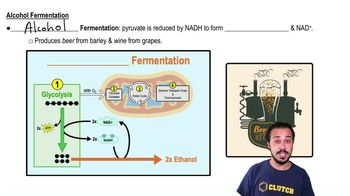
The graph shows an enzyme-catalyzed reaction.
a. Draw a line that would correspond to a noncatalyzed reaction.
b. Is this an endergonic or exergonic reaction? How can you tell?
c. Label the point on your graph that corresponds with the activation energy.