Carbolfuchsin can be used as a simple stain and a negative stain. As a simple stain, the pH is:
a. 2
b. Higher than the negative stain
c. Lower than the negative stain
d. The same as the negative stain

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

Carbolfuchsin can be used as a simple stain and a negative stain. As a simple stain, the pH is:
a. 2
b. Higher than the negative stain
c. Lower than the negative stain
d. The same as the negative stain
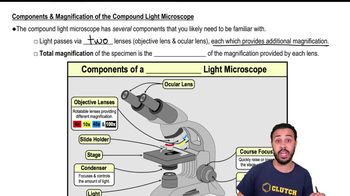
Calculate the total magnification of the nucleus of a cell being observed through a compound light microscope with a 10x ocular lens and an oil immersion lens.
Looking at the cell of a photosynthetic microorganism, you observe the chloroplasts are green in brightfield microscopy and red in fluorescence microscopy. You conclude:
a. Chlorophyll is fluorescent
b. The magnification has distorted the image
c. You’re not looking at the same structure in both microscopes
d. The stain masked the green color
e. None of the above
Which of the following is not a functionally analogous pair of stains?
a. Nigrosin and malachite green
b. Crystal violet and carbolfuchsin
c. Safranin and methylene blue
d. Ethanol-acetone and acid-alcohol
e. All of the above pairs are functionally analogous.
Why is a mordant used in the Gram stain? In the flagella stain?
Which of the following pairs is mismatched?
a. Capsule—negative stain
b. Cell arrangement—simple stain
c. Cell size—negative stain
d. Gram stain—bacterial identification
e. None of the above