Compare and contrast the bacteriophage lytic cycle and lysogeny by addressing
(1) the rate of replication of the viral genome
(2) production of virions, and
(3) effect on the host cell.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

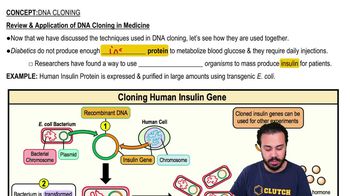
Compare and contrast the bacteriophage lytic cycle and lysogeny by addressing
(1) the rate of replication of the viral genome
(2) production of virions, and
(3) effect on the host cell.
If you come down with the flu, should your physician prescribe an antibiotic for you? Explain why or why not.
Of the viruses highlighted in Section 33.4, predict which of the following would be able to make viral proteins if nothing more than its genome were injected into a suitable host cell.
a. Pea mosaic (+ssRNA virus)
b. Bluetongue (dsRNA) virus
c. Measles (−ssRNA) virus
d. Human immunodeficiency (RNA reverse-transcribing) virus
Which of the following types of viruses would you expect to require periods of latency?
a. Viruses that have large genomes and require a long time for replication
b. Viruses that require a long time for transmission to new hosts
c. Viruses that require a long time for assembly into complex structures
d. Viruses that infect cells of the immune system
The mosquito-borne Zika virus (ZIKV) is one of the most feared viruses for pregnant women. Recent statistics justify this fear: Infants born to mothers infected with ZIKV during pregnancy face a risk of up to 42 percent of developing birth defects, including microcephaly (an abnormally small head and decreased brain volume).
What do we know about how ZIKV causes damage to the developing brain?
ZIKV is a Baltimore class IV virus. Based on this classification, what do you know about the structure of its genome?
The mosquito-borne Zika virus (ZIKV) is one of the most feared viruses for pregnant women. Recent statistics justify this fear: Infants born to mothers infected with ZIKV during pregnancy face a risk of up to 42 percent of developing birth defects, including microcephaly (an abnormally small head and decreased brain volume).
What do we know about how ZIKV causes damage to the developing brain?
Researchers have determined that host cells possess several different surface proteins that can serve as virus receptors for ZIKV. If you were to repeat the experiment described in Figure 33.8 using ZIKV instead of HIV, how would you expect the results to be different? Explain.