In Exercises 23–30, use expansion by minors to evaluate each determinant.
Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 18m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations1h 43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 5m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 22m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
7. Systems of Equations & Matrices
Determinants and Cramer's Rule
Problem 35
Textbook Question
In Exercises 31–36, use the alternative method for evaluating third-order determinants on here to evaluate each determinant. 0.50.50.5731593
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Step 1: Write down the given 3x3 determinant:
\[\left| \begin{array}{ccc} 0.5 & 7 & 5 \\ 0.5 & 3 & 9 \\ 0.5 & 1 & 3 \end{array} \right|\]
Step 2: Use the alternative method for evaluating third-order determinants, which involves expanding along the first row or using the rule of Sarrus. Here, we will use the rule of Sarrus:
- Repeat the first two columns to the right of the matrix:
\[\begin{array}{ccc|cc} 0.5 & 7 & 5 & 0.5 & 7 \\ 0.5 & 3 & 9 & 0.5 & 3 \\ 0.5 & 1 & 3 & 0.5 & 1 \end{array}\]
Step 3: Calculate the sum of the products of the diagonals from top-left to bottom-right:
\[ (0.5 \times 3 \times 3) + (7 \times 9 \times 0.5) + (5 \times 0.5 \times 1) \]
Step 4: Calculate the sum of the products of the diagonals from bottom-left to top-right:
\[ (0.5 \times 3 \times 5) + (1 \times 9 \times 0.5) + (3 \times 0.5 \times 7) \]
Step 5: Subtract the sum from Step 4 from the sum in Step 3 to find the value of the determinant:
\[ \text{Determinant} = \left[ (0.5 \times 3 \times 3) + (7 \times 9 \times 0.5) + (5 \times 0.5 \times 1) \right] - \left[ (0.5 \times 3 \times 5) + (1 \times 9 \times 0.5) + (3 \times 0.5 \times 7) \right] \]
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
3mPlay a video:
0 Comments
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Third-Order Determinants
A third-order determinant is a scalar value calculated from a 3x3 matrix. It helps determine properties like matrix invertibility and solutions to systems of equations. The determinant is computed using specific formulas or methods, such as expansion by minors or the alternative method.
Recommended video:
Guided course
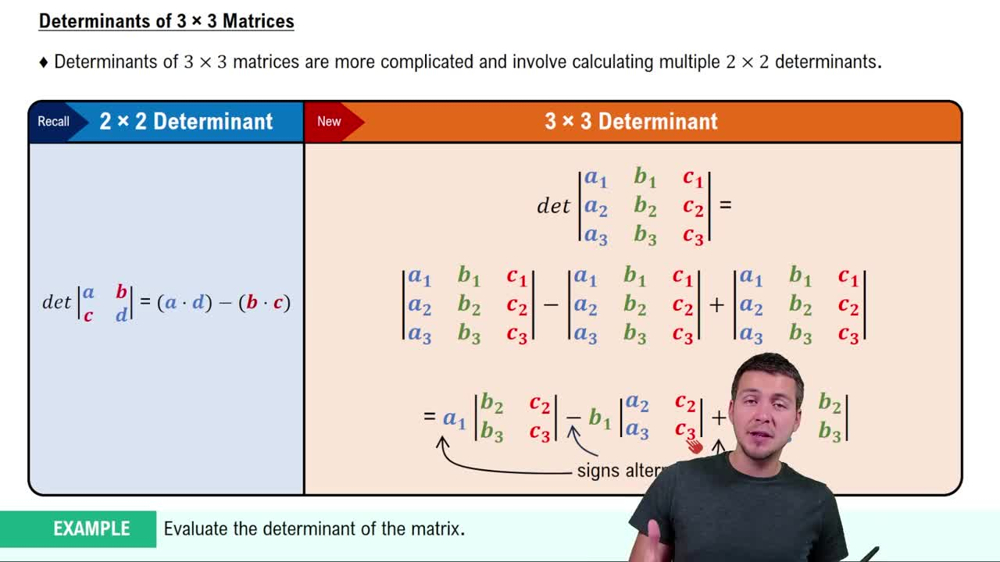
Determinants of 3×3 Matrices
Alternative Method for Evaluating Determinants
The alternative method, often called the Rule of Sarrus, is a shortcut for finding the determinant of a 3x3 matrix. It involves summing the products of diagonals from left to right and subtracting the products of diagonals from right to left, simplifying the calculation process.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Determinants of 3×3 Matrices
Matrix Representation of Systems of Equations
Matrices can represent systems of linear equations compactly, where each row corresponds to an equation and each column to a variable or constant. Evaluating the determinant of the coefficient matrix helps determine if the system has a unique solution, infinite solutions, or none.
Recommended video:
Guided course
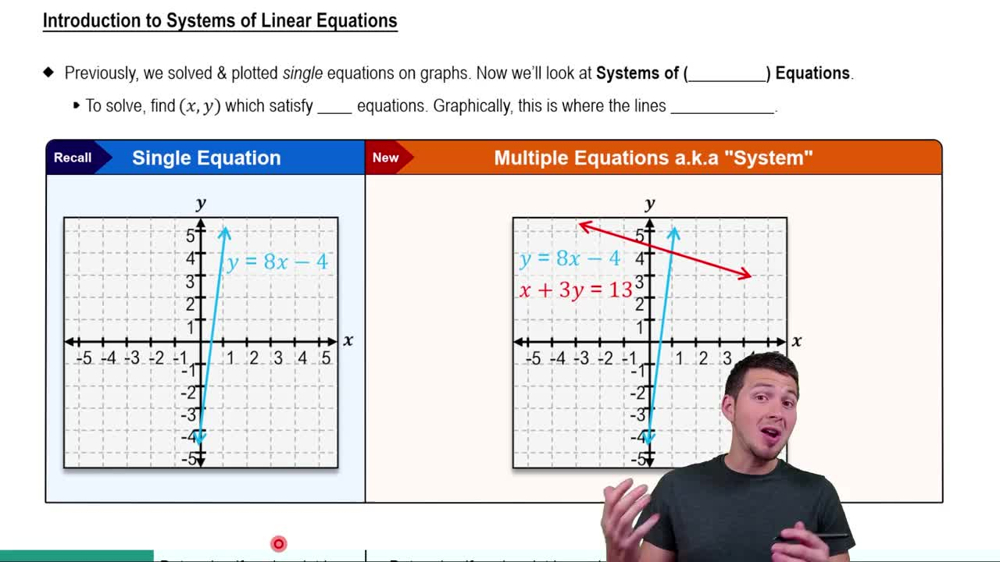
Introduction to Systems of Linear Equations
Related Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
665
views


