Textbook Question
(b) Can you identify which one between 0.10 mol ZnCl2 and 0.1M ZnCl2 contains more Zn2+ ion? Why?
407
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
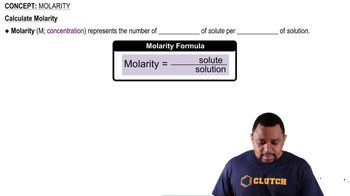


(b) Can you identify which one between 0.10 mol ZnCl2 and 0.1M ZnCl2 contains more Zn2+ ion? Why?
You make 1.000 L of an aqueous solution that contains 35.0 g of sucrose (C12H22O11). (b) How many liters of water would you have to add to this solution to reduce the molarity you calculated in part (a) by a factor of two?
(a) Calculate the molarity of a solution that contains 0.175 mol ZnCl2 in exactly 150 mL of solution.
a) Calculate the molarity of a solution made by dissolving 12.5 grams of Na2CrO4 in enough water to form exactly 750 mL of solution.
(b) How many moles of KBr are present in 150 mL of a 0.112 M solution?
(c) How many milliliters of 6.1 M HCl solution are needed to obtain 0.150 mol of HCl?