How are glycolysis and the citric acid cycle linked to the production of ATP by electron transport?
Ch.18 Metabolic Pathways and ATP Production

Timberlake13th EditionChemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryISBN: 9780134421353Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 18, Problem 56a
What is the ATP energy yield associated with each of the following?
a. FADH2 → FAD
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand the context: ATP energy yield refers to the amount of ATP generated during the electron transport chain when molecules like FADH₂ or NADH donate electrons.
Recall that FADH₂ is a coenzyme that donates electrons to the electron transport chain at Complex II, bypassing Complex I. This results in fewer protons being pumped across the mitochondrial membrane compared to NADH.
Note that the energy yield of FADH₂ is typically associated with the production of approximately 1.5 ATP molecules per molecule of FADH₂. This is due to the lower number of protons pumped and the subsequent ATP synthesis via ATP synthase.
Write the chemical reaction for the oxidation of FADH₂: . This represents the donation of electrons to the electron transport chain.
Understand that the energy yield is an approximation and can vary slightly depending on the efficiency of the electron transport chain and ATP synthase in specific cells or organisms.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
52sWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
ATP Yield from FADH₂
FADH₂ is a reduced coenzyme that plays a crucial role in cellular respiration, particularly in the electron transport chain. When FADH₂ is oxidized to FAD, it donates electrons, contributing to the generation of ATP. The typical ATP yield from one molecule of FADH₂ is approximately 1.5 ATP, as it enters the electron transport chain at a lower energy level than NADH.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Percent Yield
Electron Transport Chain (ETC)
The electron transport chain is a series of protein complexes located in the inner mitochondrial membrane that facilitate the transfer of electrons from electron donors like NADH and FADH₂ to electron acceptors. This process creates a proton gradient across the membrane, which is used by ATP synthase to produce ATP. Understanding the ETC is essential for calculating the ATP yield from various substrates.
Recommended video:
Guided course
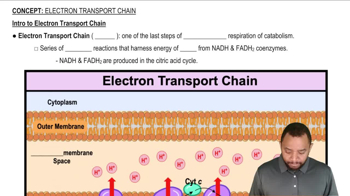
Intro to Electron Transport Chain Concept 1
Oxidative Phosphorylation
Oxidative phosphorylation is the metabolic pathway through which cells generate ATP using energy derived from the oxidation of nutrients. It involves the transfer of electrons through the ETC and the subsequent phosphorylation of ADP to ATP via ATP synthase. This process is critical for understanding how energy is produced in aerobic respiration and the specific contributions of different electron carriers like FADH₂.
Recommended video:
Guided course
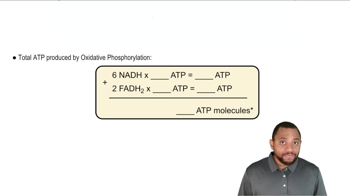
Oxidative Phosphorylation Concept 2
Related Practice
Textbook Question
1216
views
Textbook Question
What is the ATP energy yield associated with each of the following?
a. NADH → NAD+
1158
views
Textbook Question
What is the ATP energy yield associated with each of the following?
c. 2 pyruvate → 2 acetyl CoA + 2CO2
637
views
Textbook Question
Caprylic acid, CH3 ― (CH2)6 ― COOH, is a C8 fatty acid found in milk.
a. State the number of β oxidation cycles for the complete oxidation of caprylic acid.
963
views
Textbook Question
Lignoceric acid, CH3 ― (CH2)22 ― COOH, is a C24 fatty acid found in peanut oil in small amounts.
a. State the number of β oxidation cycles for the complete oxidation of lignoceric acid.
1050
views
Textbook Question
Consider the complete oxidation of oleic acid, CH3 ― (CH2)7 ― CH = CH ― (CH2)7 ― COOH, which is a C18 monounsaturated fatty acid.
a. How many cycles of β oxidation are needed?
605
views
