Textbook Question
Draw the Lewis structure for each of the following:
a. H3COCH3 (the atoms are in the order C O C)
1413
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

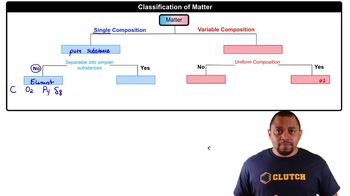

Draw the Lewis structure for each of the following:
a. H3COCH3 (the atoms are in the order C O C)
Select the more polar bond in each of the following pairs:
c. Br―Cl or S―Cl
Show the dipole arrow for each of the following bonds:
a. Si―Cl
Calculate the electronegativity difference and classify each of the following bonds as nonpolar covalent, polar covalent, or ionic:
b. C and C
Calculate the electronegativity difference and classify each of the following bonds as nonpolar covalent, polar covalent, or ionic:
c. Na and Cl
Predict the shape and polarity of each of the following molecules, which have polar covalent bonds:
a. A central atom with three identical bonded atoms and one lone pair.