The sugar d-gulose is a sweet-tasting syrup.
b. Draw the Haworth structures for α− and β-D-gulose.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


The sugar d-gulose is a sweet-tasting syrup.
b. Draw the Haworth structures for α− and β-D-gulose.
Use the Fischer projection for d-gulose in problem 13.69 to answer each of the following:
a. Draw the Fischer projection and name the product formed by the reduction of D-gulose.
Use the Fischer projection for D-gulose in problem 13.69 to answer each of the following:
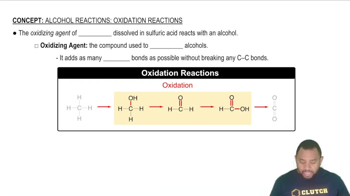
b. Draw the Fischer projection and name the product formed by the oxidation of D-gulose.
If α−galactose is dissolved in water, β−galactose is eventually present. Explain how this occurs.
α−Cellobiose is a disaccharide obtained from the hydrolysis of cellulose. It is quite similar to maltose except it has a β(1→4)−glycosidic bond. Draw the Haworth structure for α−cellobiose.
The disaccharide trehalose found in mushrooms is composed of two α-D-glucose molecules joined by an α(1→1)−glycosidic bond. Draw the Haworth structure for trehalose.