When pyruvate is used to form acetyl CoA, the product has only two carbon atoms. What happened to the third carbon?
Ch.18 Metabolic Pathways and ATP Production

Timberlake13th EditionChemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryISBN: 9780134421353Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 18, Problem 92a
What metabolic substrate(s) can be produced from the carbon atoms of each of the following amino acids?
a. histidine
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Step 1: Understand the question. The problem asks which metabolic substrates can be produced from the carbon atoms of the amino acid histidine. This involves identifying the metabolic pathways histidine participates in and the products formed.
Step 2: Recall the metabolic fate of histidine. Histidine is an amino acid that can be broken down in the body through catabolic pathways. Its carbon skeleton is converted into intermediates that enter central metabolic pathways.
Step 3: Identify the key intermediate produced from histidine. Histidine is primarily converted into α-ketoglutarate, a key intermediate in the citric acid cycle (also known as the Krebs cycle or TCA cycle). This conversion occurs after histidine is deaminated and undergoes further enzymatic reactions.
Step 4: Relate α-ketoglutarate to metabolic substrates. α-Ketoglutarate can be used in the citric acid cycle to produce energy (ATP) or serve as a precursor for gluconeogenesis, leading to the production of glucose. It can also contribute to the synthesis of other biomolecules.
Step 5: Summarize the metabolic substrates derived from histidine. The carbon atoms of histidine can ultimately contribute to the production of glucose (via gluconeogenesis) or energy (via the citric acid cycle). Additionally, they may be used for biosynthesis of other compounds depending on cellular needs.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
3mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
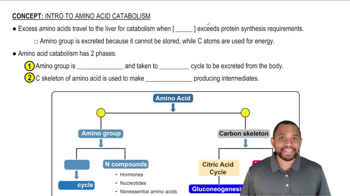
Amino Acid Metabolism
Amino acid metabolism involves the biochemical processes that break down amino acids for energy or convert them into other compounds. Each amino acid can be deaminated, leading to the production of various metabolic substrates, such as glucose or fatty acids, depending on the specific amino acid and the body's needs.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Amino Acid Catabolism: Amino Group Example 2
Histidine Catabolism
Histidine is an essential amino acid that can be catabolized to produce several metabolites, including histamine and α-ketoglutarate. The breakdown of histidine involves several enzymatic reactions, ultimately contributing to the synthesis of important biomolecules and energy production in the body.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Intro to Amino Acid Catabolism Concept 1
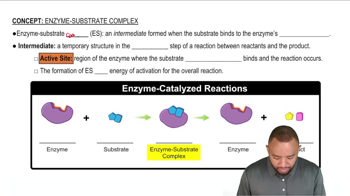
Metabolic Substrates
Metabolic substrates are the molecules that serve as the starting materials for metabolic pathways. In the context of amino acids, these substrates can include intermediates that enter the citric acid cycle or precursors for gluconeogenesis, which are crucial for energy production and maintaining metabolic balance.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Enzyme-Substrate Complex Concept 1
Related Practice
Textbook Question
1000
views
Textbook Question
If there are no reactions in the citric acid cycle that use oxygen, O2, why does the cycle operate only in aerobic conditions?
746
views
Textbook Question
In the chemiosmotic model, how is energy provided to synthesize ATP?
1589
views
Textbook Question
What metabolic substrate(s) can be produced from the carbon atoms of each of the following amino acids?
d. phenylalanine
636
views
Textbook Question
One cell at work may break down 2 million (2 000 000) ATP molecules in one second. Some researchers estimate that the human body has about 1013 cells.
b. If ATP has a molar mass of 507 g/mole, how many grams of ATP are hydrolyzed in one day?
1033
views
Textbook Question
State if each of the following processes release or require ATP:
f. first six reactions of glycolysis
647
views
