Match the diagrams with the following:
b. a nonpolar solute and a polar solvent
<IMAGE>

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


Match the diagrams with the following:
b. a nonpolar solute and a polar solvent
<IMAGE>
If all the solute is dissolved in diagram 1, how would heating or cooling the solution cause each of the following changes?
a. 2 to 3
<IMAGE>
Select the diagram that represents the solution formed by a solute <IMAGE> that is a (9.2)
a. nonelectrolyte
<IMAGE>
Select the container that represents the dilution of a 4% (m/v) KCl solution to give each of the following:
a. a 2% (m/v) KCl solution
<IMAGE>
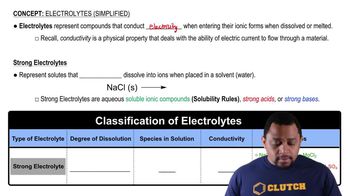
A pickle is made by soaking a cucumber in brine, a salt-water solution. What makes the smooth cucumber become wrinkled like a prune?
A semipermeable membrane separates two compartments, A and B. If the levels in A and B are equal initially, select the diagram that illustrates the final levels in a to d:
<IMAGE>