Textbook Question
Describe the difference(s) among saturated fatty acids, unsaturated fatty acids, and polyunsaturated fatty acids.
867
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
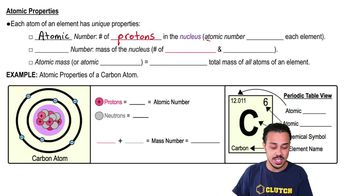

Describe the difference(s) among saturated fatty acids, unsaturated fatty acids, and polyunsaturated fatty acids.
Common long-term energy storage molecules are __________ , __________ , __________ , and __________.
Which of the following is not an organic compound?
a. Monosaccharide
b. Formaldehyde
c. Water
d. Steroid
Which of the following terms most correctly describes the bonds in a molecule of water?
a. Nonpolar covalent bond
b. Polar covalent bond
c. Ionic bond
d. Hydrogen bond
Groups of atoms such as NH₂ or OH that appear in certain common arrangements are called __________ .
Explain how the polarity of water molecules makes water an excellent solvent.