Why do we breathe oxygen and give off carbon dioxide?

Why do cyanobacteria and algae take in carbon dioxide and give off oxygen?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Photosynthesis
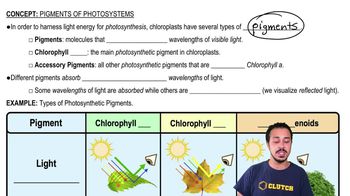
Role of Chlorophyll and Pigments

Carbon Dioxide Fixation

Microbes that reduce N2 to NH3 engage in nitrogen ___________ .
Activation energy ______.
a. Is the amount of energy required during an activity such as flagellar motion
b. Requires the addition of nutrients in the presence of water
c. Is lowered by the action of organic catalysts
d. Results from the movement of molecules
Coenzymes are _______.
a. Types of apoenzymes
b. Proteins
c. Inorganic cofactors
d. Organic cofactors
What happens to the carbon atoms in sugar catabolized by Escherichia coli?
Which of the following statements best describes ribozymes?
a. Ribozymes are proteins that aid in the production of ribosomes.
b. Ribozymes are nucleic acids that produce ribose sugars.
c. Ribozymes store enzymes in ribosomes.
d. Ribozymes process RNA molecules in eukaryotes.
