In a neuron, what creates the electrochemical gradient favoring the outflow of K+ when the cell is at rest?
a. Na+/K+-ATPase
b. Voltage-gated K+ channels
c. Voltage-gated Na+ channels
d. Ligand-gated Na+/K+ channels

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


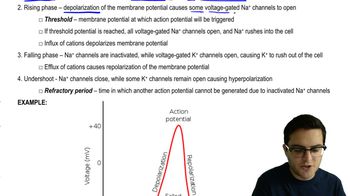
In a neuron, what creates the electrochemical gradient favoring the outflow of K+ when the cell is at rest?
a. Na+/K+-ATPase
b. Voltage-gated K+ channels
c. Voltage-gated Na+ channels
d. Ligand-gated Na+/K+ channels
Which of the following brain regions is responsible for the formation of new memories?
a. Brainstem
b. Cerebellum
c. Frontal lobe
d. Hippocampus
Explain the difference between a ligand-gated K+ channel and a voltage-gated K+ channel.
Compare and contrast the somatic nervous system and autonomic nervous system.
Why is memory thought to involve changes in particular synapses?
a. At some synapses, more neurotransmitters are released after learning takes place.
b. At some synapses, a different type of neurotransmitter is released after learning takes place.
c. When researchers stimulated certain neurons electrically, individuals replayed memories.
d. When researchers changed synapses in the brains of patients during surgery, the patients' memories changed.
Explain why drugs that prevent neurotransmitters from being taken back up by a presynaptic neuron have dramatic effects on the activity of postsynaptic neurons.