Solve each equation in Exercises 15–34 by the square root property. (4x - 1)2 = 16
Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 18m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations1h 43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 5m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 22m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
1. Equations & Inequalities
Intro to Quadratic Equations
Problem 43
Textbook Question
In Exercises 35–46, determine the constant that should be added to the binomial so that it becomes a perfect square trinomial. Then write and factor the trinomial.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the coefficient of the linear term in the binomial. Here, the binomial is \(x^2 - \frac{2}{3}x\), so the coefficient of \(x\) is \(-\frac{2}{3}\).
Take half of the coefficient of \(x\). Half of \(-\frac{2}{3}\) is \(-\frac{1}{3}\).
Square the result from step 2. Squaring \(-\frac{1}{3}\) gives \(\left(-\frac{1}{3}\right)^2 = \frac{1}{9}\).
Add this squared value to the original binomial to form a perfect square trinomial: \(x^2 - \frac{2}{3}x + \frac{1}{9}\).
Write the trinomial as a squared binomial using the form \((x + a)^2 = x^2 + 2ax + a^2\). Here, it factors as \(\left(x - \frac{1}{3}\right)^2\).
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
4mPlay a video:
0 Comments
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Perfect Square Trinomial
A perfect square trinomial is a quadratic expression that can be factored into the square of a binomial, typically in the form (a + b)^2 = a^2 + 2ab + b^2. Recognizing or creating such trinomials helps simplify factoring and solving quadratic expressions.
Recommended video:

Solving Quadratic Equations by Completing the Square
Completing the Square
Completing the square involves adding a constant term to a quadratic expression to form a perfect square trinomial. This constant is found by taking half the coefficient of the linear term, squaring it, and adding it to the expression, enabling easier factoring or solving.
Recommended video:

Solving Quadratic Equations by Completing the Square
Factoring Quadratic Expressions
Factoring quadratic expressions means rewriting them as a product of binomials or squares of binomials. After completing the square, the trinomial can be factored into (x + d)^2 form, which simplifies solving equations or analyzing the function.
Recommended video:
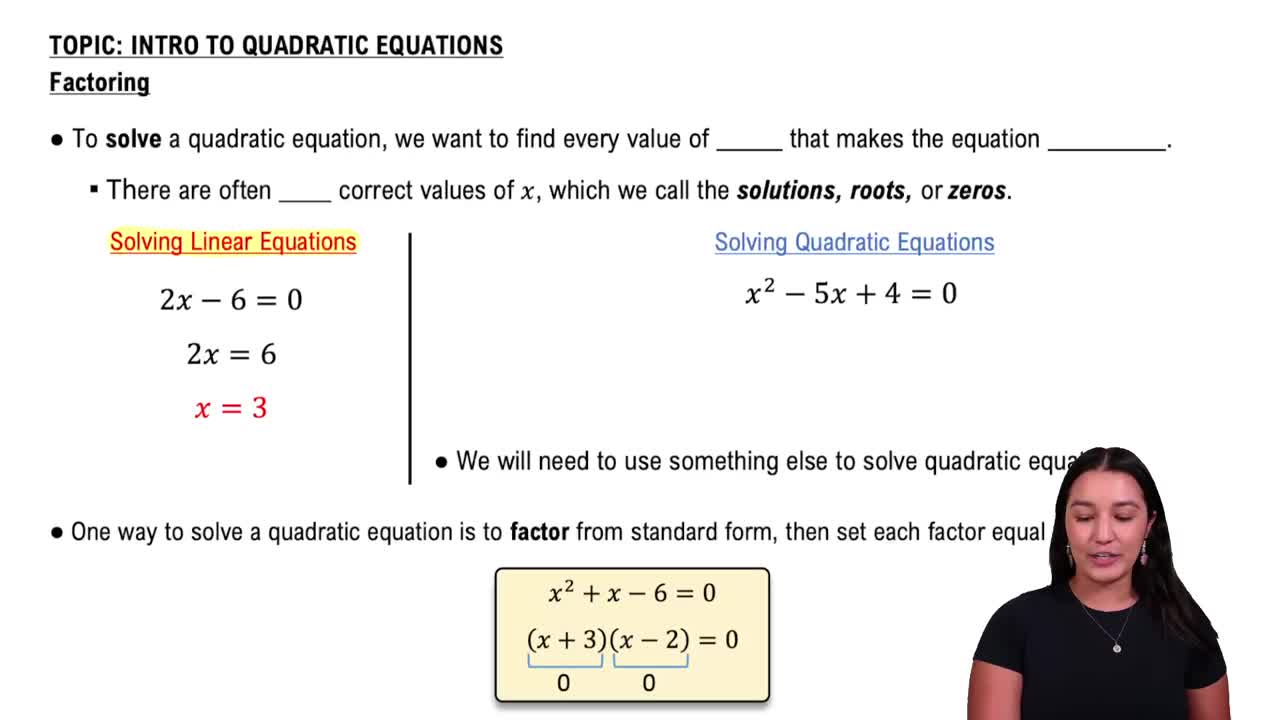
Solving Quadratic Equations by Factoring

 5:35m
5:35mWatch next
Master Introduction to Quadratic Equations with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
593
views
