Find the domain of each rational function. g(x)=3x2/(x−5)(x+4)
Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 18m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations1h 43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 5m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 22m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
5. Rational Functions
Asymptotes
Problem 13
Textbook Question
Use the graph of the rational function in the figure shown to complete each statement in Exercises 9–14.
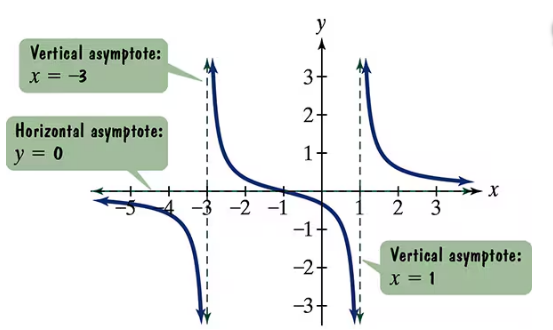
As _____
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the horizontal asymptote from the graph. The horizontal asymptote is the line that the function approaches as \(x\) goes to positive or negative infinity. In this graph, the horizontal asymptote is given as \(y = 0\).
Recall that for rational functions, the behavior of \(f(x)\) as \(x \to -\infty\) (or \(x \to \infty\)) is determined by the horizontal asymptote, if one exists.
Since the horizontal asymptote is \(y = 0\), this means that as \(x\) becomes very large in the negative direction, the function values \(f(x)\) approach 0.
Therefore, you can complete the statement: As \(x \to -\infty\), \(f(x) \to 0\).
This means the function values get closer and closer to zero but do not necessarily equal zero for very large negative \(x\).
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
1mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Vertical Asymptotes
Vertical asymptotes occur where the function approaches infinity or negative infinity as the input approaches a specific value. They represent values of x where the function is undefined, often due to division by zero in rational functions. In the graph, vertical asymptotes are shown at x = 6 and x = 14.
Recommended video:

Determining Vertical Asymptotes
Horizontal Asymptotes
A horizontal asymptote describes the behavior of a function as x approaches positive or negative infinity. It indicates the value that the function approaches but does not necessarily reach. In this graph, the horizontal asymptote is y = 0, meaning as x goes to ±∞, f(x) approaches 0.
Recommended video:

Determining Horizontal Asymptotes
End Behavior of Rational Functions
The end behavior of a rational function describes how the function behaves as x approaches infinity or negative infinity. It is often determined by the degrees of the numerator and denominator polynomials. Here, since the horizontal asymptote is y = 0, as x → -∞, f(x) → 0.
Recommended video:
End Behavior of Polynomial Functions

 6:24m
6:24mWatch next
Master Introduction to Asymptotes with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
910
views
