Use transformations of f(x)=1/x or f(x)=1/x2 to graph each rational function. g(x)=1/(x+2)2
Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 18m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations1h 43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 5m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 22m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
5. Rational Functions
Asymptotes
Problem 61
Textbook Question
Graph each rational function. ƒ(x)=(x+1)/(x-4)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the rational function given: \(f(x) = \frac{x+1}{x-4}\).
Determine the vertical asymptote by finding the values of \(x\) that make the denominator zero. Set \(x - 4 = 0\) and solve for \(x\).
Find the horizontal asymptote by comparing the degrees of the numerator and denominator. Since both numerator and denominator are degree 1, the horizontal asymptote is the ratio of the leading coefficients.
Calculate the \(x\)-intercept by setting the numerator equal to zero and solving for \(x\), i.e., solve \(x + 1 = 0\).
Calculate the \(y\)-intercept by evaluating \(f(0)\), which means substituting \(x = 0\) into the function.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
12mPlay a video:
0 Comments
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Rational Functions
A rational function is a ratio of two polynomials, expressed as f(x) = P(x)/Q(x), where Q(x) ≠ 0. Understanding the domain restrictions and behavior of these functions is essential, as they often have asymptotes and discontinuities where the denominator is zero.
Recommended video:
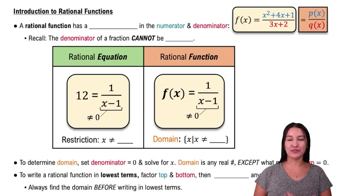
Intro to Rational Functions
Vertical and Horizontal Asymptotes
Vertical asymptotes occur where the denominator equals zero, indicating values excluded from the domain. Horizontal asymptotes describe the end behavior of the function as x approaches infinity or negative infinity, determined by comparing the degrees of the numerator and denominator polynomials.
Recommended video:

Determining Horizontal Asymptotes
Graphing Rational Functions
Graphing involves identifying intercepts, asymptotes, and behavior near these lines. Plot key points, analyze limits near asymptotes, and use symmetry or transformations to sketch the curve accurately, providing a visual understanding of the function's behavior.
Recommended video:
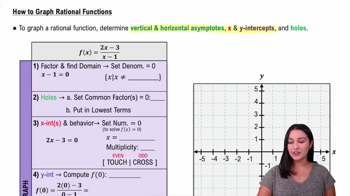
How to Graph Rational Functions
Related Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
785
views


