Express the given function h as a composition of two functions ƒ and g so that h(x) = (fog) (x). h(x) = ∛(x² – 9)
Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 18m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations1h 43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 5m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 22m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
3. Functions
Intro to Functions & Their Graphs
Problem 86a
Textbook Question
Use the graphs of f and g to solve Exercises 83–90.
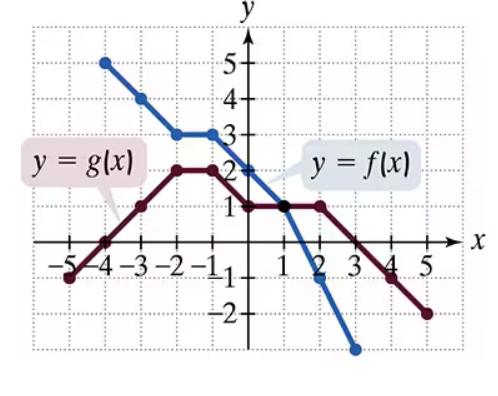
Find(g/f)(3)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Step 1: Understand the problem. You are tasked with finding (g/f)(3), which means you need to evaluate the function g(x) divided by f(x) at x = 3.
Step 2: Locate x = 3 on the graph. Look at the vertical line corresponding to x = 3 and identify the y-values of both f(x) (blue graph) and g(x) (red graph).
Step 3: Determine the value of g(3). From the graph, find the y-coordinate of the red graph at x = 3.
Step 4: Determine the value of f(3). From the graph, find the y-coordinate of the blue graph at x = 3.
Step 5: Divide g(3) by f(3). Use the values obtained in Steps 3 and 4 to compute g(3)/f(3). Ensure that f(3) is not zero to avoid division by zero.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
1mPlay a video:
0 Comments
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Function Notation
Function notation is a way to represent functions in mathematics, typically using symbols like f(x) and g(x). Here, f and g are functions, and x is the input variable. Understanding function notation is essential for interpreting and manipulating functions, especially when performing operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, or division.
Recommended video:

Interval Notation
Graph Interpretation
Interpreting graphs involves analyzing the visual representation of functions to extract information about their behavior. In this case, the graphs of f(x) and g(x) provide insights into their values at specific points, such as x = 3. This skill is crucial for solving problems that require evaluating functions based on their graphical representations.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Graphs and Coordinates - Example
Division of Functions
The division of functions, denoted as (g/f)(x), represents the quotient of two functions g(x) and f(x). To find (g/f)(3), one must evaluate g(3) and f(3) from their respective graphs and then compute the ratio g(3)/f(3). This concept is fundamental in algebra as it allows for the exploration of relationships between different functions.
Recommended video:

Multiplying & Dividing Functions

 5:2m
5:2mWatch next
Master Relations and Functions with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
942
views
