For ƒ(x) = 3x and g(x)= (1/4)x find each of the following. Round answers to the nearest thousandth as needed. g(2)
Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 18m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations1h 43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 5m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 22m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions
Introduction to Exponential Functions
Problem 23
Textbook Question
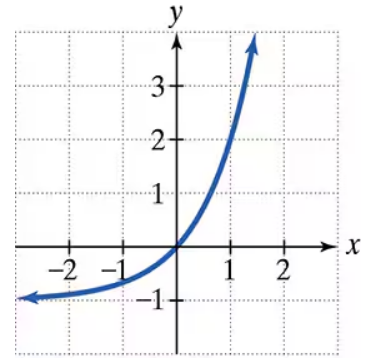
The graph of an exponential function is given. Select the function for each graph from the following options:
f(x)=3x,g(x)=3x−1,h(x)=3x−1,f(x)=−3x,G(x)=3−x,H(x)=−3−x.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Step 1: Identify the general shape of the graph. The graph shows a decreasing curve that approaches zero as x increases, which is characteristic of an exponential decay function.
Step 2: Recall the given function options: \(f(x) = 3^x\), \(g(x) = 3^{x-1}\), \(h(x) = 3^x - 1\), \(f(x) = -3^x\), \(G(x) = 3^{-x}\), and \(H(x) = -3^{-x}\). Notice that functions with \$3^x\( grow exponentially, while those with \)3^{-x}$ decay exponentially.
Step 3: Since the graph is decreasing and approaches zero as x increases, focus on functions with negative exponents, such as \(G(x) = 3^{-x}\) and \(H(x) = -3^{-x}\).
Step 4: Check the sign of the function values. The graph is above the x-axis (positive values), so the function is positive. This rules out \(H(x) = -3^{-x}\), which would be negative.
Step 5: Verify the y-intercept by substituting \(x=0\) into \(G(x) = 3^{-x}\). This gives \(G(0) = 3^0 = 1\). Compare this with the graph's y-intercept to confirm the match.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
1mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Exponential Functions and Their Graphs
Exponential functions have the form f(x) = a^x, where the base a is positive and not equal to 1. Their graphs show rapid growth or decay, depending on the base and the exponent's sign. Understanding the shape and behavior of these graphs helps identify the function from its graph.
Recommended video:

Graphs of Exponential Functions
Transformations of Exponential Functions
Transformations include shifts and reflections. Horizontal shifts occur when the exponent is modified (e.g., 3^(x-1) shifts the graph right by 1), vertical shifts occur when a constant is added or subtracted outside the function (e.g., 3^x - 1 shifts down by 1), and reflections occur when the function is multiplied by -1 or the exponent is negated.
Recommended video:

Transformations of Exponential Graphs
Identifying Decreasing vs. Increasing Exponential Functions
An exponential function with a base greater than 1 and a positive exponent is increasing, while if the exponent is negative or the function is multiplied by -1, the graph decreases. Recognizing whether the graph is increasing or decreasing is key to matching it with the correct function.
Recommended video:

Graphs of Exponential Functions

 6:13m
6:13mWatch next
Master Exponential Functions with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
581
views
