Solve each polynomial inequality in Exercises 1–42 and graph the solution set on a real number line. Express each solution set in interval notation. (x−4)(x+2)>0
Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 18m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations1h 43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 5m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 22m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
1. Equations & Inequalities
Linear Inequalities
Problem 9
Textbook Question
Solve each polynomial inequality in Exercises 1–42 and graph the solution set on a real number line. Express each solution set in interval notation. x2−6x+9<0
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Recognize that the inequality is a quadratic inequality: \(x^2 - 6x + 9 < 0\).
Factor the quadratic expression on the left side. Notice that \(x^2 - 6x + 9\) is a perfect square trinomial, so it factors as \((x - 3)^2\).
Rewrite the inequality using the factorization: \((x - 3)^2 < 0\).
Consider the properties of squares: since \((x - 3)^2\) is always greater than or equal to zero for all real \(x\), it can never be less than zero.
Conclude that there are no real values of \(x\) that satisfy \((x - 3)^2 < 0\), so the solution set is the empty set, which in interval notation is \(\emptyset\).
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
4mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Polynomial Inequalities
Polynomial inequalities involve expressions where a polynomial is compared to zero or another value using inequality symbols like <, >, ≤, or ≥. Solving them requires finding the values of the variable that make the inequality true, often by analyzing the sign of the polynomial over different intervals.
Recommended video:

Linear Inequalities
Factoring Quadratic Expressions
Factoring is the process of rewriting a quadratic expression as a product of two binomials. For example, x² - 6x + 9 factors to (x - 3)(x - 3). Factoring helps identify the roots of the polynomial, which are critical points for determining where the inequality changes sign.
Recommended video:
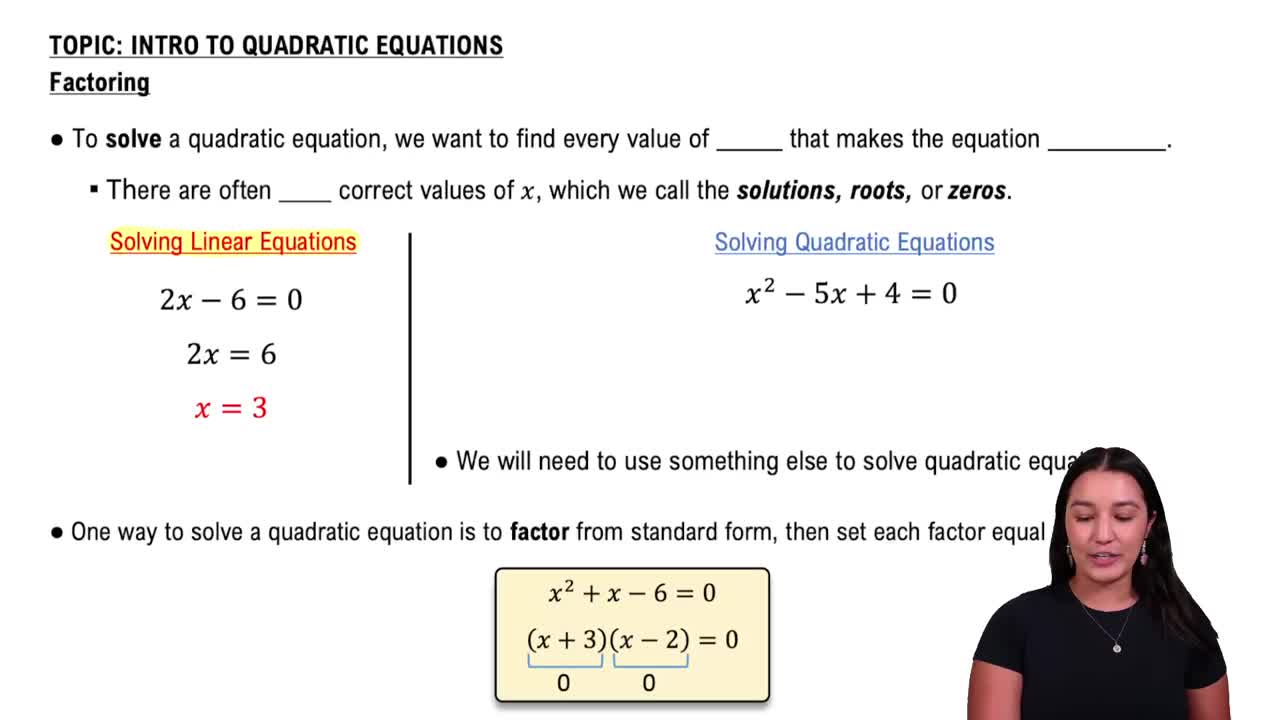
Solving Quadratic Equations by Factoring
Interval Notation and Number Line Graphing
Interval notation is a concise way to represent sets of real numbers, especially solution sets of inequalities. Graphing on a number line visually shows where the polynomial is positive or negative. Together, they help communicate the solution clearly, indicating which intervals satisfy the inequality.
Recommended video:

Interval Notation
Related Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
455
views


