Back
BackProblem 3
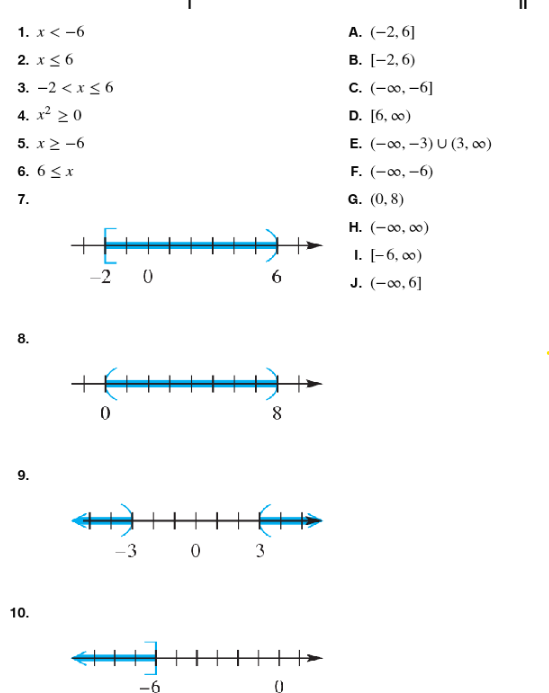
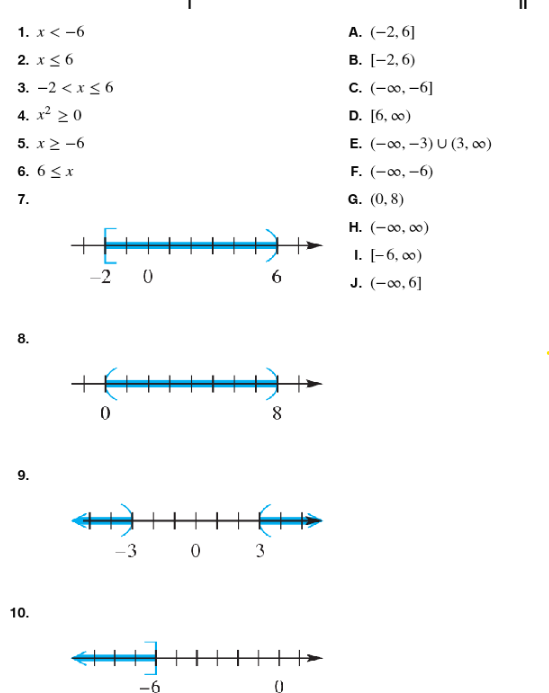
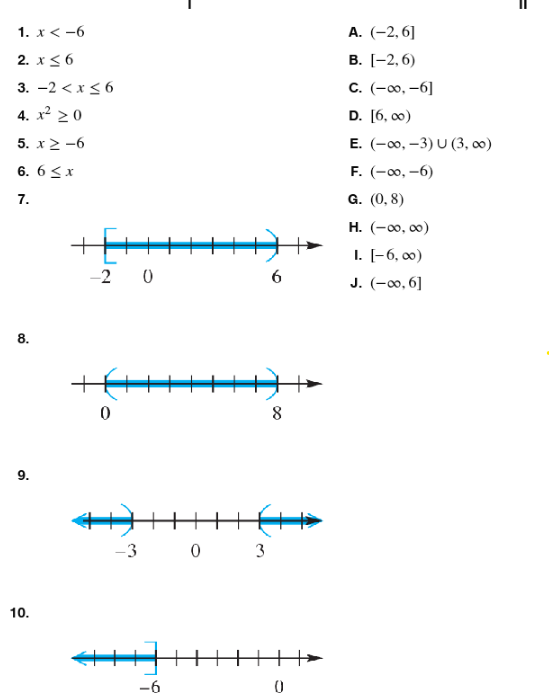
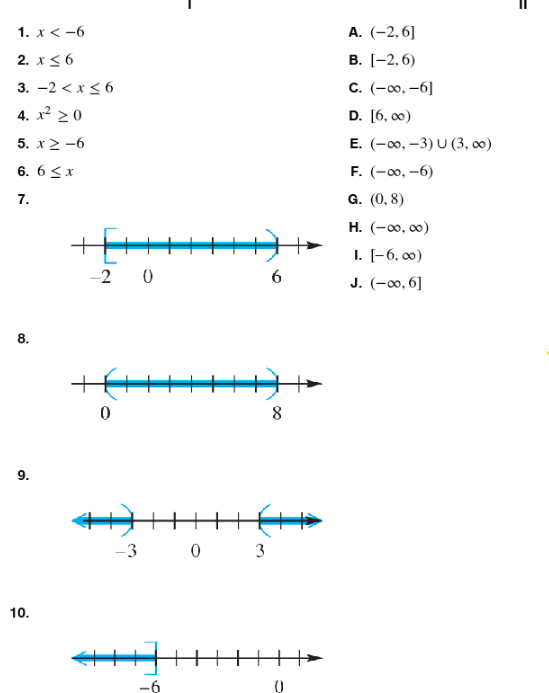
Match the inequality in each exercise in Column I with its equivalent interval notation in Column II. -2 < x ≤ 6
Problem 4
Match the inequality in each exercise in Column I with its equivalent interval notation in Column II. x2≥0
Problem 5
Match the inequality in each exercise in Column I with its equivalent interval notation in Column II . x≥-6
Problem 6
Match the inequality in each exercise in Column I with its equivalent interval notation in Column II. 6≤x
Problem 17
Solve each inequality. Give the solution set in interval notation. 3(x+5)+1≥5+3x
Problem 18
Solve each inequality. Give the solution set in interval notation. 6x-(2x+3)≥4x-5
Problem 19
Solve each inequality. Give the solution set in interval notation. 8x-3x+2<2(x+7)
Problem 20
Solve each inequality. Give the solution set in interval notation. 2-4x+5(x-1)<-6(x-2)
Problem 21
Solve each inequality. Give the solution set in interval notation. (4x+7)/-3≤2x+5
Problem 22
Solve each inequality. Give the solution set in interval notation. (2x-5)/-8≤1-x
Problem 23
Solve each inequality. Give the solution set in interval notation. (1/3)x+(2/5)x-(1/2)(x+3)≤1/10
Problem 24
Solve each inequality. Give the solution set in interval notation. -(2/3)x-(1/6)x+(2/3)(x+1)≤4/3
Problem 29
Solve each inequality. Give the solution set in interval notation. -5<5+2x<11
Problem 31
Solve each inequality. Give the solution set in interval notation. 10≤2x+4≤16
Problem 34
Solve each inequality. Give the solution set in interval notation. 2>-6x+3>-3
Problem 35
Solve each inequality. Give the solution set in interval notation. -4≤(x+1)/2≤5
Problem 38
Solve each inequality. Give the solution set in interval notation. 1≤(4x-5)/2<9
Problem 39
Solve each quadratic inequality. Give the solution set in interval notation.. x2+3x-4<0
Problem 40
Solve each quadratic inequality. Give the solution set in interval notation. x2-7x+10<0
Problem 41
Solve each quadratic inequality. Give the solution set in interval notation. x2-x-6>0
Problem 42
Solve each quadratic inequality. Give the solution set in interval notation. x2-7x+10>0
Problem 43
Solve each quadratic inequality. Give the solution set in interval notation. 2x2-9x≤18
Problem 44
Solve each quadratic inequality. Give the solution set in interval notation. 3x2+x≤4
Problem 47
Solve each quadratic inequality. Give the solution set in interval notation. x(x-1)≤6
Problem 48
Solve each quadratic inequality. Give the solution set in interval notation. x(x+1)<12
Problem 49
Solve each quadratic inequality. Give the solution set in interval notation. x2≤9
Problem 50
Solve each quadratic inequality. Give the solution set in interval notation. x2>16
Problem 52
Solve each quadratic inequality. Give the solution set in interval notation. 4x2+3x+1≤0
Problem 53
Solve each quadratic inequality. Give the solution set in interval notation. x2-2x≤1
Problem 54
Solve each quadratic inequality. Give the solution set in interval notation. x2+4x>-1