In Exercises 1–14, express each interval in set-builder notation and graph the interval on a number line. [- 5, 2)
Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 18m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations1h 43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 5m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 22m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
1. Equations & Inequalities
Linear Inequalities
Problem 5
Textbook Question
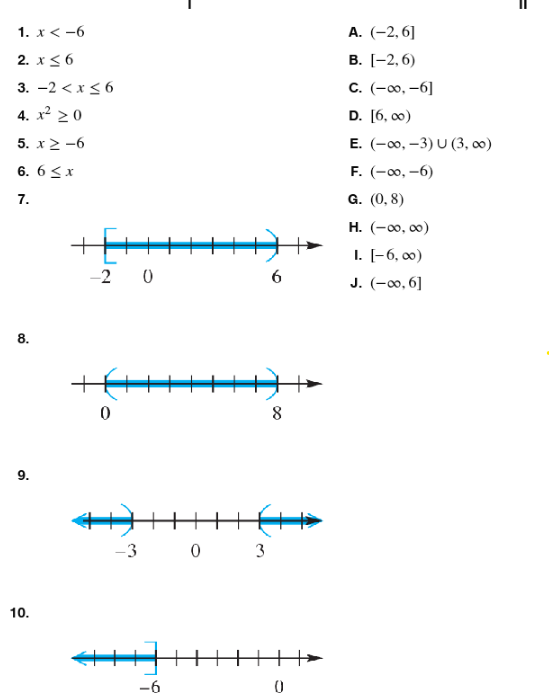
Match the inequality in each exercise in Column I with its equivalent interval notation in Column II . x≥-6
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the inequality given: \(x \geq -6\). This means \(x\) is greater than or equal to \(-6\).
Recall that interval notation uses brackets and parentheses to represent ranges of values. A square bracket \([\) or \(]\) means the endpoint is included (closed interval), while a parenthesis \((\) or \()\) means the endpoint is not included (open interval).
Since the inequality includes \(x \geq -6\), the number \(-6\) is included in the solution set, so we use a square bracket on the left side.
The inequality \(x \geq -6\) means \(x\) can be any number from \(-6\) up to positive infinity. Infinity is never included, so we use a parenthesis on the right side.
Write the interval notation as \([-6, \infty)\) to represent all \(x\) values greater than or equal to \(-6\).
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
1mPlay a video:
0 Comments
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Inequalities and Their Symbols
Inequalities express the relationship between two values using symbols like ≥, ≤, >, and <. The symbol ≥ means 'greater than or equal to,' indicating all values greater than or exactly equal to a given number. Understanding these symbols is essential to translate inequalities into interval notation.
Recommended video:

Linear Inequalities
Interval Notation
Interval notation is a concise way to represent sets of numbers on the number line. It uses brackets [ ] to include endpoints and parentheses ( ) to exclude them. For example, x ≥ -6 corresponds to the interval [-6, ∞), including -6 and all numbers greater than it.
Recommended video:

Interval Notation
Matching Inequalities to Interval Notation
Matching involves identifying the correct interval notation that represents a given inequality. This requires understanding the inequality's direction and whether endpoints are included, then selecting the interval with appropriate brackets and bounds that reflect the inequality accurately.
Recommended video:

Interval Notation
Related Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
1729
views


