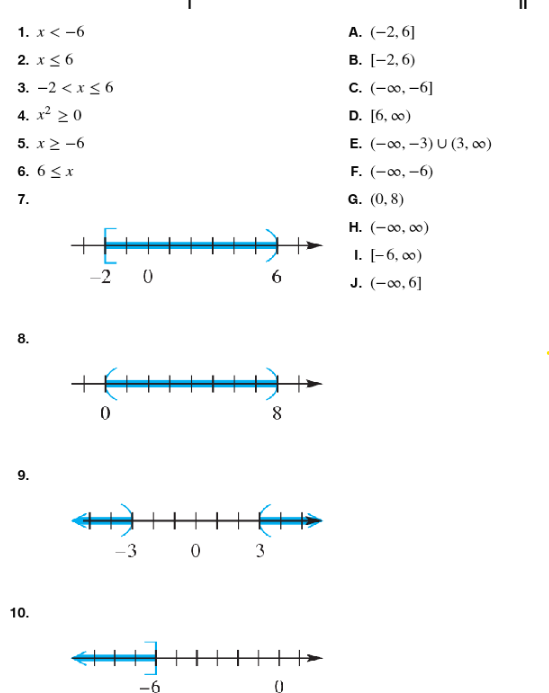
Match the inequality in each exercise in Column I with its equivalent interval notation in Column II. x<-6
Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 18m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations1h 43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 5m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 22m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
1. Equations & Inequalities
Linear Inequalities
Problem 3
Textbook Question
Match the inequality in each exercise in Column I with its equivalent interval notation in Column II. -2 < x ≤ 6
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the inequality given: \(-2 < x \leq 6\). This means \(x\) is greater than \(-2\) but less than or equal to \$6$.
Recall that interval notation uses parentheses \(()\) for strict inequalities (less than or greater than) and brackets \([]\) for inclusive inequalities (less than or equal to or greater than or equal to).
Since \(x\) is strictly greater than \(-2\), use a parenthesis for the left endpoint: \((-2\).
Since \(x\) is less than or equal to \$6\(, use a bracket for the right endpoint: \)6]$.
Combine these to write the interval notation as \((-2, 6]\), which represents all \(x\) values between \(-2\) and \$6\(, not including \)-2\( but including \)6$.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
1mPlay a video:
0 Comments
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Inequalities
Inequalities express a range of values that satisfy a condition, using symbols like <, ≤, >, and ≥. Understanding how to interpret and manipulate these symbols is essential for translating between inequality notation and interval notation.
Recommended video:

Linear Inequalities
Interval Notation
Interval notation represents sets of numbers between two endpoints, using parentheses () for exclusive bounds and brackets [] for inclusive bounds. It provides a concise way to describe solution sets of inequalities.
Recommended video:

Interval Notation
Relationship Between Inequalities and Interval Notation
Converting inequalities to interval notation requires recognizing whether endpoints are included or excluded based on ≤ or < symbols. For example, -2 < x ≤ 6 translates to the interval (-2, 6], where -2 is excluded and 6 is included.
Recommended video:

Interval Notation
Related Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
663
views


